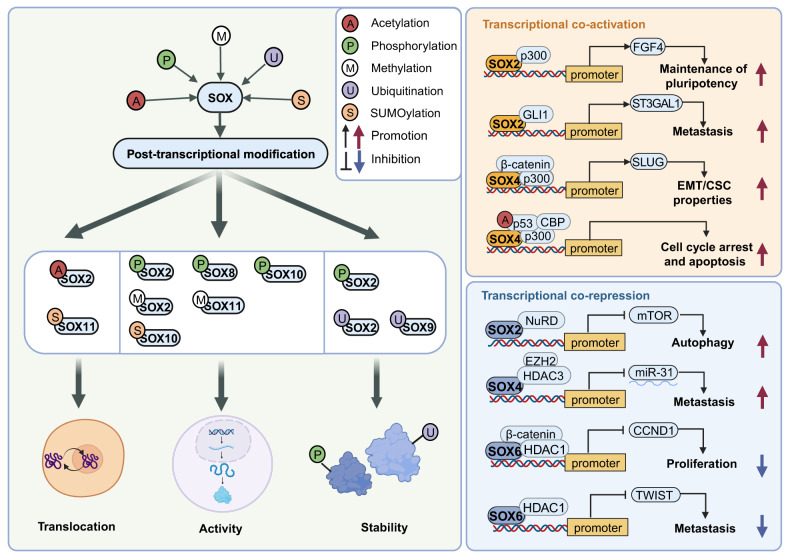
Fig. 2. Post-transcriptional modifications and cofactors of SOX TFs.
Post-transcriptional modification of SOX TFs mainly includes acetylation [48], phosphorylation [41, 42, 120], methylation [40, 59], ubiquitination [45, 46] and SUMOylation [43, 44], which infects the translocation, activity and stability of SOX TFs. Cofactors interact with SOX TFs and exert co-activation [50–53] or co-repression [54–57] effects on the physiological and pathological functions of SOX TFs.