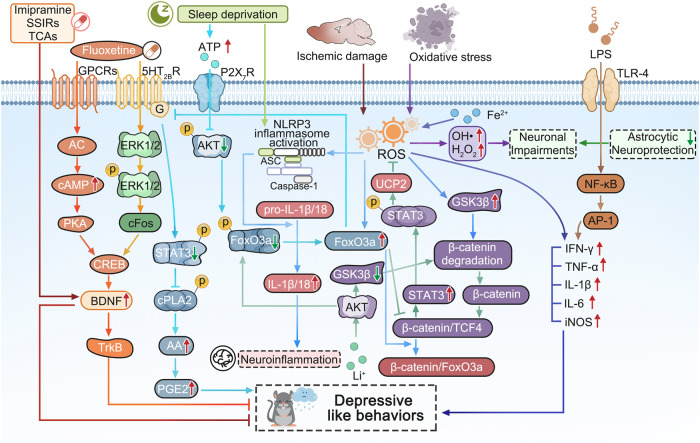
Fig. 3.
The molecular signaling schematic of cytokine hypothesis in the pathogenesis of MDD. The rodent performed the depressive like behaviors are impaired by some widely accepted risk factors, such as long-term sleep deprivation (SD), oxidative stress, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), ischemic damage and so on. Long-term SD can increase the extracellular ATP level, the latter inhibits the activation of AKT and the followed phosphorylation of FoxO3a by stimulating P2X7 receptors (P2X7R), the dephosphorylated FoxO3a translocates into the astrocytic nucleus, then the increased FoxO3a decreases the expression of 5-HT2BR expression, which results the reduced phosphorylation of STAT3 which increases the activation of cPLA2 and the followed release of arachidonic acid (AA) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), finally causing the depressive-like behaviors.41 Thus, antidepressant fluoxetine activates ERK1/2/cFos pathway by stimulating 5-HT2BR and AC/cAMP/PKA pathway by activating GPCRs in order to increase the activation of CREB and the level of BDNF and TrkB, which can alleviate the depressive like behaviors induced by long-term SD.147,148 As well as, imipramine, other SSIRs, and TCAs can also play antidepressive roles by increasing BDNF mRNA expression in astrocytes.148 Ischemic stroke can trigger the increase of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which can induce the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and the release of IL-1β/18, resulting in the neuroinflammation, however, Li+ salt inhibits the activation of GSK3β and increases the phosphorylation of FoxO3a by activating AKT, which promotes the more FoxO3a transportation from nucleus into cytoplasm, and the reduced FoxO3a in nucleus lacks the competition with TCF4, the increased complex level of β-catenin and TCF4 further stimulates the expression and the phosphorylation of STAT3, which further induce the mRNA and protein expression of UCP2, then in mitochondrion, the increased UCP2 suppresses the production of ROS and results in the deactivation of NLRP3 inflammasomeincreases.136 Superoxidation of Fe2+ stimulates an increase in ROS, resulting in the production of inflammatory cytokines (including IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS).138 While, the treatments of oxidative stress (OS) can produce a large number of ROS, such as OH• and H2O2, resulting in neuronal impairments, while astrocytes can play their neuroprotective role by antioxidation.135 Additionally, LPS can also increase TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 by TLR-4/NFkB/AP-1 pathway and cause depressive-like behavior.142 Adobe Illustrator was used to generate this figure