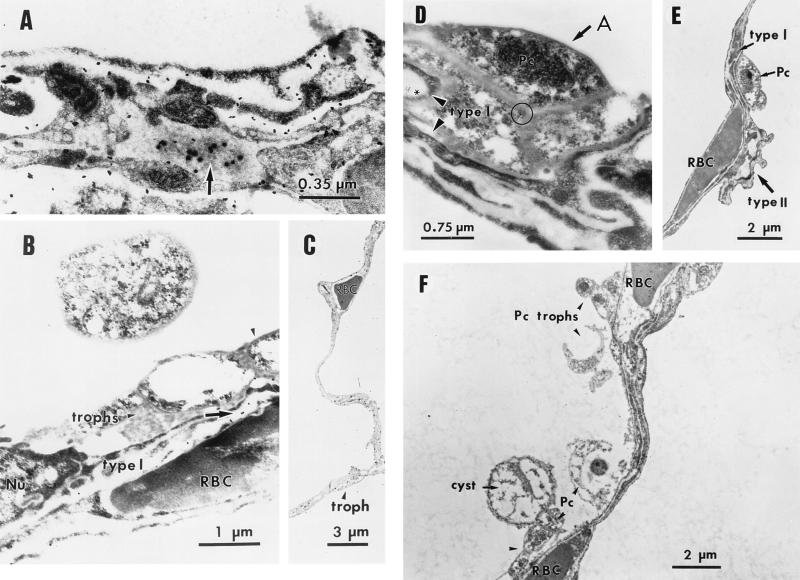
FIG. 4.
IEM localization of FBG in the lung epithelium. The intracellular presence of FBG in P. carinii-infected lung tissue was determined by IEM by using 100 μg of anti-FBG IgG/ml detected with Protein-A-gold (diameter, 20 nm) conjugate (panels A and B, arrows; panel D, asterisk). FBG was detected at the junction of cell membranes of trophic forms of P. carinii organisms (panel D, circle) aggregated (panel D, arrow) along the alveolar epithelium (panel D, arrowheads). Purified rabbit IgG (100 μg/ml) was used as the negative control in the primary antibody step (F). The morphologically rigid cyst and pleomorphic trophic forms of P. carinii organisms attached to type I epithelium and aggregated in the alveolar spaces are shown in panels B to F. Lower magnifications show the integrity of septal walls between alveoli (C and F). Alveolar capillaries are indicated by the presence of the erythrocytes (RBC). The appropriate magnification for each field is indicated. A, alveolar lumen; Nu, nucleus; Pc, P. carinii.