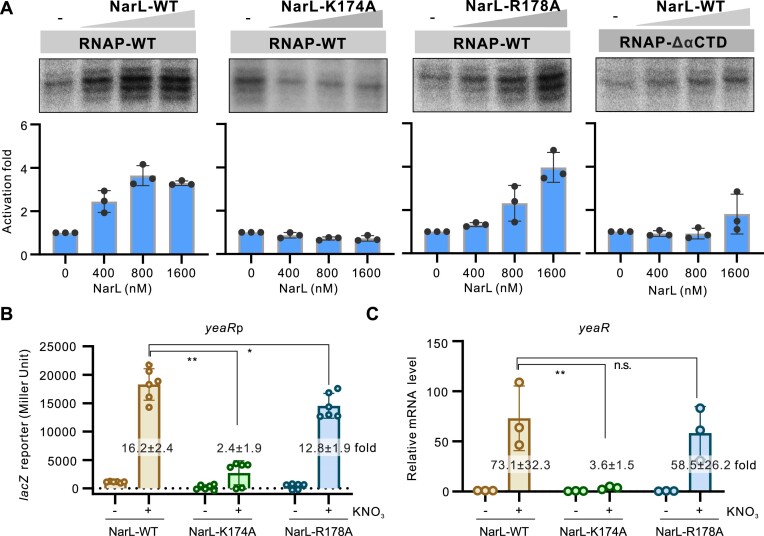
Figure 4.
Roles of key residues of NarL involved in interacting with RNAP in transcription activation. (A) Roles of NarL–RNAP interaction in NarL-activated transcription. In vitro transcription using purified E. coli RNAP with wild-type (WT) or mutated NarL protein on yeaR promoter was applied. The Lys174 residue was mutated to alanine and named as K174A. The Arg178 residue was mutated to alanine and named as R178A. The αCTD deleted RNAP (RNAP–ΔαCTD) was also purified and applied in this assay. RNA products were quantified from three experiments and are shown as mean ± SD in the bottom panel. (B) Activities of yeaRp in E. coli strain expressing WT or mutated NarL protein. The yeaRp was fused with lacZ reporter gene and the expression of lacZ was measured by β-galactosidase test. Bacteria were grown to late logarithmic growth phase at 37°C with or without 1% KNO3. Individual values of biological replicates (n = 6) are shown as dots, and the mean ± SD values are displayed as error bars. ** P < 0.01.* P < 0.05. (C) Transcriptional level of yeaR gene in E. coli strain expressing wild type or mutated NarL protein under the same conditions as in panel B. The transcriptional levels were analyzed by RT-qPCR assay. The mRNA levels of 16S rRNA in each strain was used for normalization, and the relative level of yeaR mRNA in E. coli WT strain without KNO3 induction was normalized to 1. In panels B and C, the activation fold by WT or mutated NarL to yeaRp activity in the presence of 1% KNO3 compared with WT strain without KNO3 was indicated in each column.