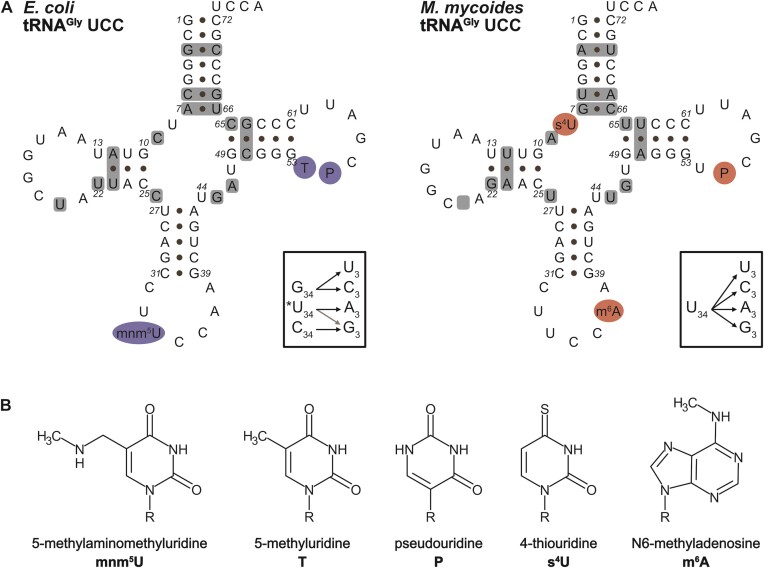
Figure 1.
tRNA sequences and modifications. (A) Secondary structure of tRNAGly UCC from E. coli and M. mycoides. Decoding of the four synonymous glycine codons (GGN) in E. coli requires three tRNAGly isoacceptors with the anticodons CCC, GCC, and *UCC (left box; ‘*’ modified U). In contrast, the M. mycoides tRNAGly with the anticodon UCC is capable of decoding the four GGN codon (right box). Grey shaded boxes in the tRNA structures indicate the sequence differences between the E. coli and M. mycoides tRNAGly UCC. The D-arm of the M. mycoides tRNA is one nucleotide smaller compared to E. coli (indicated by an empty grey box). The modified positions are highlighted in blue (E. coli) or red (M. mycoides). (B) The chemical structures of the indicated tRNA modifications decorating the tRNAs are depicted.