| PFO |
q
t
= qe(1 − e−K1t) (7) |
- qt and qe (mg g−1): the adsorbed amount of copper at any time “t” and at the end, respectively |
Fig. 8
|
| PSO |
 (8) (8) |
- K1 (min−1), K2 (g (min−1 mg−1)), kAV (min−1): the constants of PFO, PSO and Avrami, respectively |
Fig. 8
|
| Elovich |
 (9) (9) |
- α (mg (g−1 min−1)): the sorption rate constant associated with the covered surface of chemisorption in the Elovich kinetic model |
Fig. 8
|
| - β (mg g−1): the desorption constant associated with the reaction energy of chemisorption in the Elovich kinetic model |
| Avrami |
 (10) (10) |
- nAV: the Avrami constant exponent (dimensionless) |
Fig. 8
|
| Intraparticle diffusion |
 (11) (11) |
- Kint (mg (g−1 min−1/2)): rate constant of the Weber–Morris model |
Fig. 8
|
| -C (mg g−1): constant depending on the boundary layer thickness in the Weber–Morris kinetic model |
| Langmuir |
 (12) (12) |
- Qmax (mg g−1): maximum adsorption capacity of Langmuir |
Fig. 9
|
| - KL (L mg−1): the constants of Langmuir |
| Freundlich |
 (13) (13) |
- KF [(mg g−1)/(mg L−1)1/n]: the constants of Freundlich |
Fig. 9
|
| - nF: dimensionless Freundlich parameter of intensity |
| Redlich–Peterson |
 (14) (14) |
-KRP (L g−1) and aRP (mg L−1)−g: the Redlich–Peterson equilibrium constants, respectively |
Fig. 9
|
| - g: the dimensionless Redlich–Peterson exponent should be ≤1 |
| Sips |
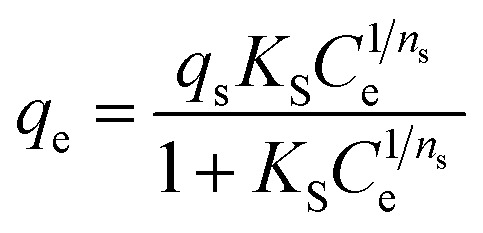 (15) (15) |
- qs and Qmax (mg g−1): the maximum adsorption capacity of Sips and Liu isotherms, respectively |
Fig. 9
|
| Liu |
 (16) (16) |
- KS and Kg (L mg−1): the Sips and Liu equilibrium constants, respectively |
Fig. 9
|
| - ns and nL: the dimensionless Sips and Liu exponents, respectively |
 (8)
(8) (9)
(9) (10)
(10) (11)
(11) (12)
(12) (13)
(13) (14)
(14)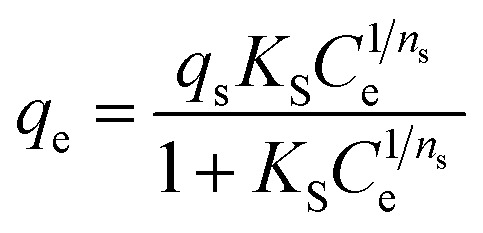 (15)
(15) (16)
(16)