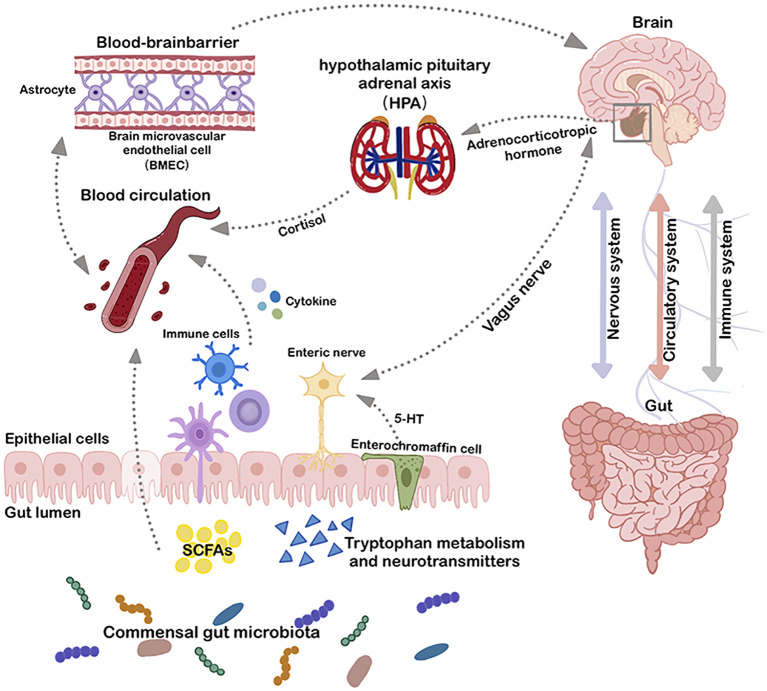
Figure 1.
Microbiota-gut-brain axis. The bidirectional connection between the gut and the brain involves three major systems: the immune system, the circulatory system, and the nervous system. Multiple direct (e.g. vagus nerve) and indirect (e.g. short-chain fatty acids, cytokines, and key dietary amino acids, such as tryptophan) pathways exist to modulate the CNS with gut microbiota and to affect the gut microbial environment through the CNS. BMEC, brain microvascular endothelial cell; HPA, hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; 5-HT, 5-Hydroxytryptamine.