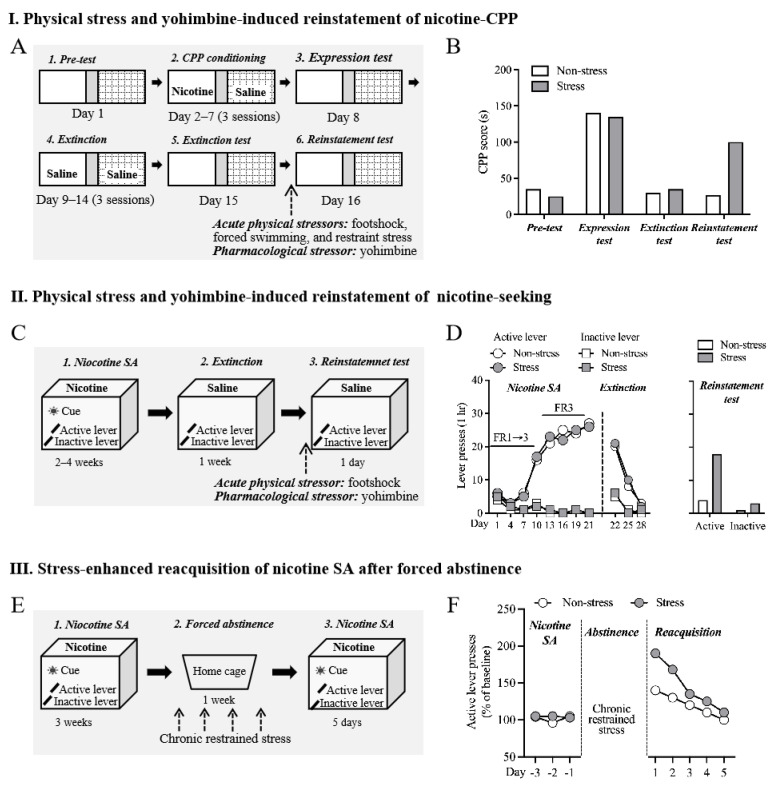
Figure 1.
Animal models of stress-induced nicotine relapse. (A) Schematic procedure of physical stress- and yohimbine-induced reinstatement of nicotine CPP. Animals underwent pre-test, conditioning, expression test, extinction, extinction test, and reinstatement test of nicotine CPP. Acute physical stress or yohimbine were given immediately before the reinstatement test. (B) Representative of behavioral data. Stressed animals showed a higher level of preference for the nicotine-paired side during the reinstatement test. (C) Schematic procedure of physical stress- and yohimbine-induced reinstatement of nicotine-seeking. Animals underwent nicotine self-administration, extinction, and reinstatement test. Acute physical stress or yohimbine were given immediately before the reinstatement of the nicotine-seeking test. Active but not inactive lever was paired with intravenous nicotine administration. (D) Representative of behavioral data. Stressed animals showed an increase in active lever presses during the reinstatement test. (E) Schematic procedure of stress-enhanced reacquisition of nicotine SA after forced abstinence. Animals underwent long-access nicotine self-administration (23 h/day), forced abstinence in the home cage, and nicotine self-administration again (reacquisition). Chronic restrained stress was conducted during the force abstinence period. (F) Representative of behavioral data. Compared to non-stressed animals, stressed animals showed higher levels of active presses during the reacquisition phase. CPP: conditioned place preference; SA: self-administration.