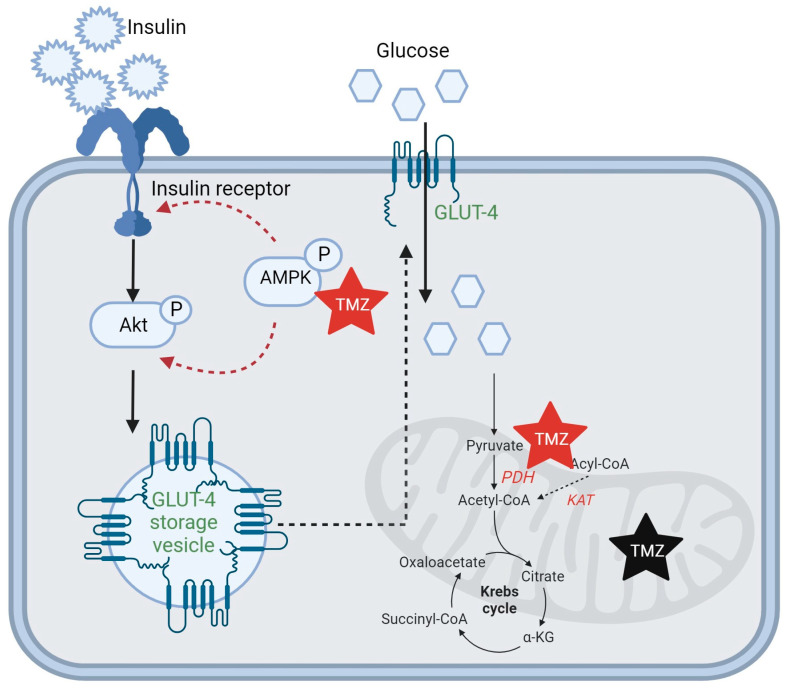
Figure 4.
TMZ mechanism of action. TMZ is an inhibitor of KAT, decreasing fatty acid β-oxidation, and an activator of PDH, an enzyme that catalyzes the transformation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, making it a metabolic modulator from using fatty acids as a source of energy to glucose. TMZ activates AMPK and Akt through phosphorylation. GLUT-4 insulin-activated receptors for glucose are externalized from storage vesicles to the cell membrane. (TMZ–trimetazidine, KAT–3 ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, Akt–protein kinase B, GLUT-4-insulin-regulated glucose transporter, AMPK–AMP-activated protein kinase, PDH–pyruvate dehydrogenase). Red stars represent an activator effect and black star represents an inhibitor effect of TMZ on specific enzymes. A red dotted arrow signifies a process involving several steps activated by TMZ and a black dotted arrow signifies a process involving several steps inhibited by TMZ.