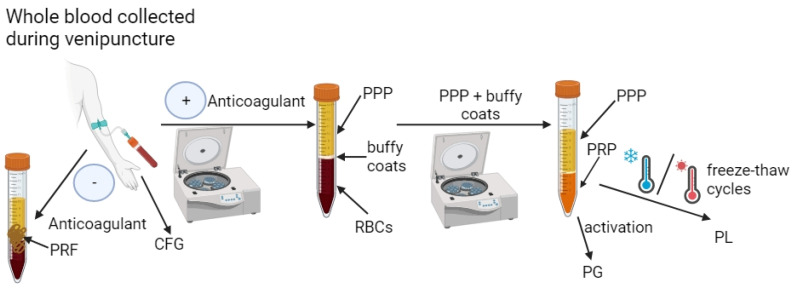
Figure 2.
Scheme of obtaining platelet concentrates (PCs). After collecting blood from the patient’s vein into a test tube with an anticoagulant, it is centrifuged to obtain three phases: platelet-poor plasma (PPP), buffy coats and red blood cells (RBCs). To obtain platelet-rich plasma (PRP), PPP and buffy coats are usually subjected to subsequent centrifugation. The PRP can then be subjected to activation by, e.g., thrombin or calcium chloride to obtain platelet gel (PG) or to freeze–thaw cycles to obtain platelet lysate (PL). In turn, after collecting the patient’s blood into a tube without anticoagulant and centrifuging it, platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) or concentrated growth factors (CGF) are obtained depending on the centrifugation parameters used. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 19 January 2024).