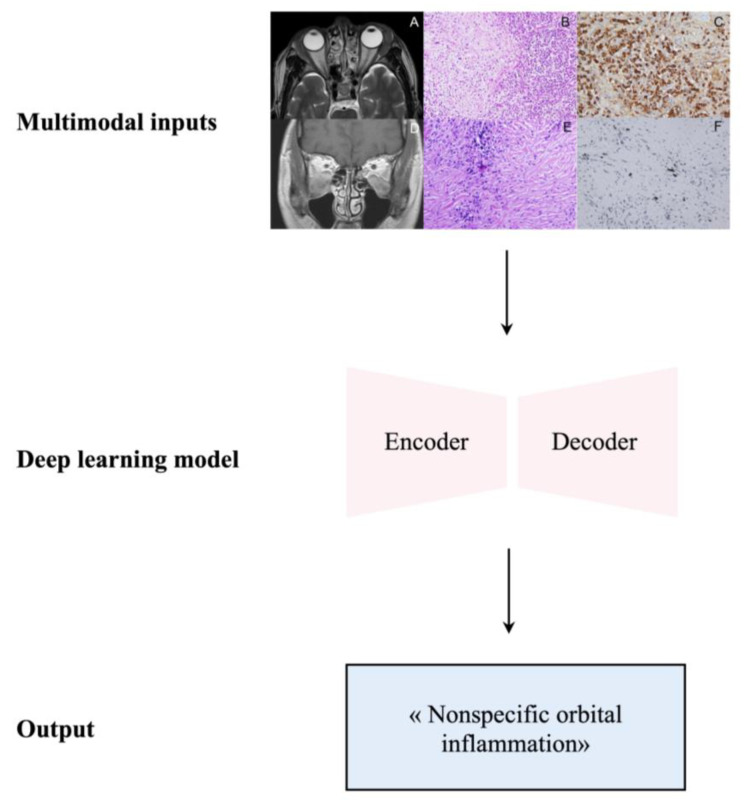
Figure 6.
Overview of deep learning applications for connecting images to texts. The use of deep learning in the diagnosis of nonspecific orbital inflammation (NSOI) has shown great success. By using multimodal inputs (i.e., imaging results, such as CT orbits and orbit MRIs, or histopathology results from biopsies), the architecture can output the correct diagnosis, therefore leveraging the challenges associated with the non-accurate diagnosis of NSOI. Multimodal inputs can be (A) T2-weighted MRI image of lacrimal glands, (B) histopathological slide showing lymphoplasmacytic infiltration of a lacrimal gland, (C) positive IgG4 immunostaining, (D) T1 enhanced MRI image of the orbits, (E) histopathological slide with lymphocytic infiltration, or (F) negative IgG4 immunostaining. Parts of this figure (multimodal inputs) were reprinted from Non-specific orbital inflammation: Current understanding and unmet needs, 81, Lee et al. 100885 [1], Copyright (2021), with permission from Elsevier.