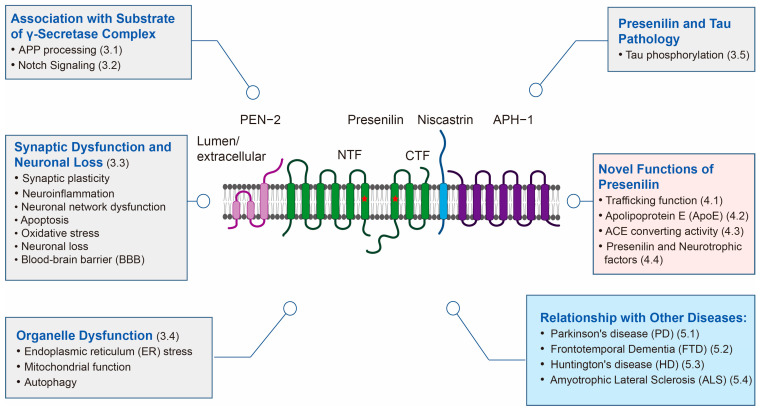
Figure 1.
Multifaceted Roles of Presenilin in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Comprehensive Diagram. This diagram illustrates the diverse functions of presenilin in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders. Grey boxes represent functions associated with presenilin contributing to AD through γ-secretase substrates, neuron loss, and organelle dysfunction. Pink boxes highlight novel functions of presenilin, indicating potential mechanisms. Blue boxes depict the relationships between presenilin and other degenerative diseases. In the center, the γ-secretase complex’s subunits and their membrane topologies are displayed. During complex maturation, presenilin undergoes proteolytic processing, resulting in amino-terminal fragment (NTF) and carboxy-terminal fragment (CTF). The catalytic aspartic acid residues in NTF and CTF are marked with stars. Additional subunits include Nicastrin, APH-1, and PEN-2.