Figure 3.
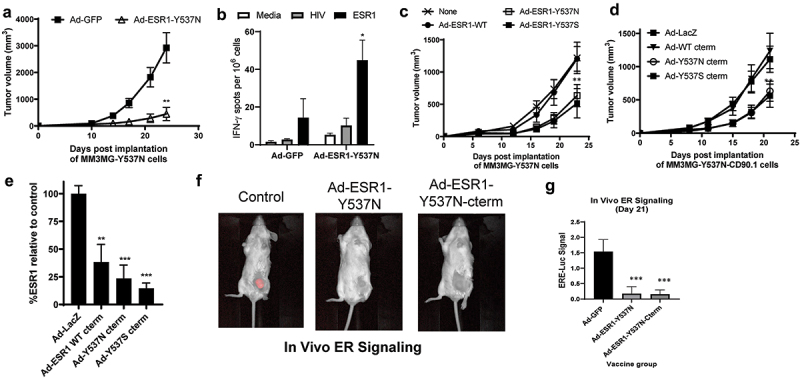
Anti-tumor impact of ESR1mut vaccines in a ERmut+ mouse mammary tumor model. (a) BALB/c mice were vaccinated with indicated virus and MM3MG-ESR1-Y537N cells were implanted two weeks post-vaccination and tumor growth measured biweekly. (b) spleens from mice in (a) were assessed by IFNγ ELISPOT assay (n = 5 mice/group). (c,d) BALB/c mice were implanted with MM3MG-ESR1-Y537N (c) or MM3MG-ESR1-Y537N-CD90.1 (d) expressing cells and vaccinated the following day with tumor growth measured bi-weekly (n = 5 mice/group). (e) Tumors from (d) were removed and CD90.1 expression was measured ex vivo as a surrogate of ESR1 expression. Shown as % of expression seen in control treated cells. Error bars represent SEM. *p < .05; **p < .05; ***p < .001. (f,g) Representative images and analysis (g) of MM3MG-ESR1-Y537N-CD90.1/ERE-Luc tumors vaccinated with ad-GFP control or ad-ESR1-Y537N as in (c,d).
