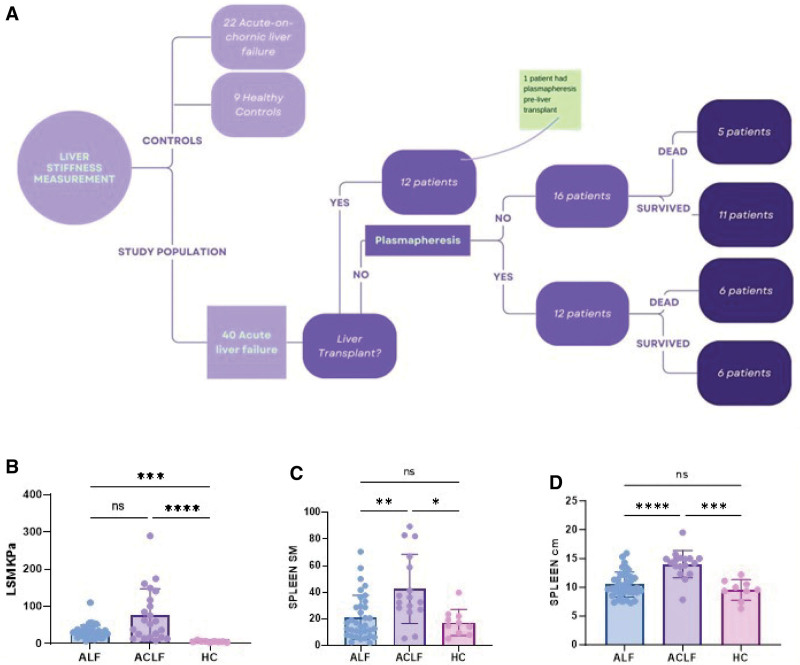
Figure 1.
Study population and main findings. A, Flowchart including the study population. B, Admission liver stiffness measurement of the right lobe (RLSM) accurately identified healthy control (HC) individuals (5.6 ± 2 kPa), acute liver failure (31.7 ± 17), and acute-on-chronic liver failure (76.3 ± 71 kPa) patients (Kruskall-Wallis). Acute liver failure (ALF) (n = 40), acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) (n = 22), HC individuals (n = 9). C, Spleen size is increased in ACLF (14 ± 2.3 cm) compared with ALF (10.4 ± 2 cm) and HC individuals (9.5 ± 1.8 cm) (Kruskall-Wallis). III, Spleen stiffness is increased in ACLF (45.6 ± 26 kPa) compared with ALF (21 ± 16 kPa) and HC individuals (17.3 ± 10 kPa) (Kruskall-Wallis). D, Spleen stiffness is increased in ACLF (45.6 ± 26 kPa) compared with ALF (21 ± 16 kPa) and HC individuals (17.3 ± 10 kPa) (Kruskall-Wallis). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. ns = not statistically significant.