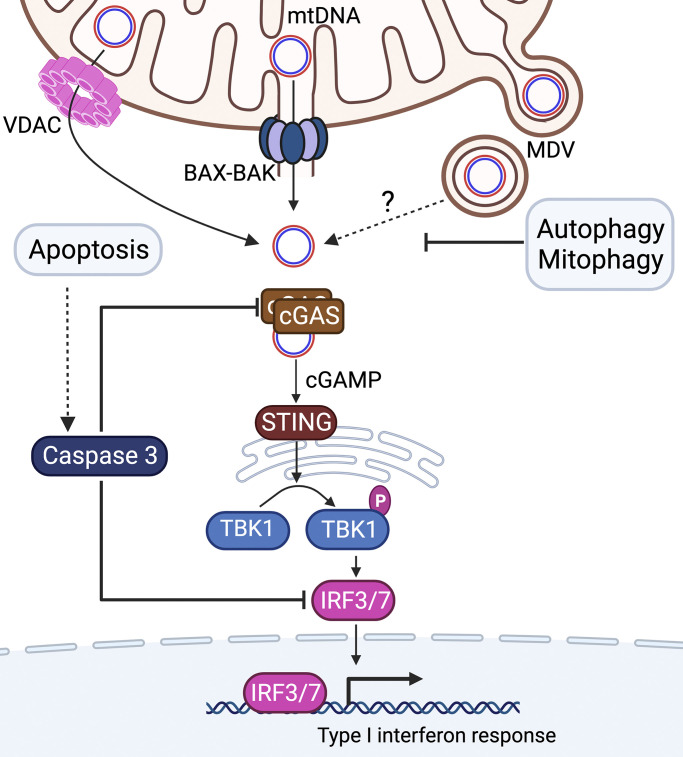
Figure 3.
Accumulation of mtDNAs in the cytosol stimulates the cGAS-STING-mediated immune response. mtDNAs reside in the mitochondrial matrix. However, mtDNAs enter the cytosol upon pore formation in the mitochondrial outer membrane by VDAC oligomerization or BAX–BAK assembly. Mitochondrial-derived vesicles (MDVs) can form during mitochondrial stress, providing a third route by which mtDNAs exit mitochondria. In the cytosol, mtDNAs stimulate cGAS, which generates cGAMP to activate STING, which phosphorylates TBK1. In turn, the transcription factors IRF3 and IRF7 induce the type I interferon immune response. Importantly, apoptosis along with caspase 3 antagonizes the interferon response by cleaving cGAS, IRF3, and IRF7. Mitophagy also antagonizes the response by degrading damaged mitochondria which limits the accumulation of mtDNAs in the cytosol.