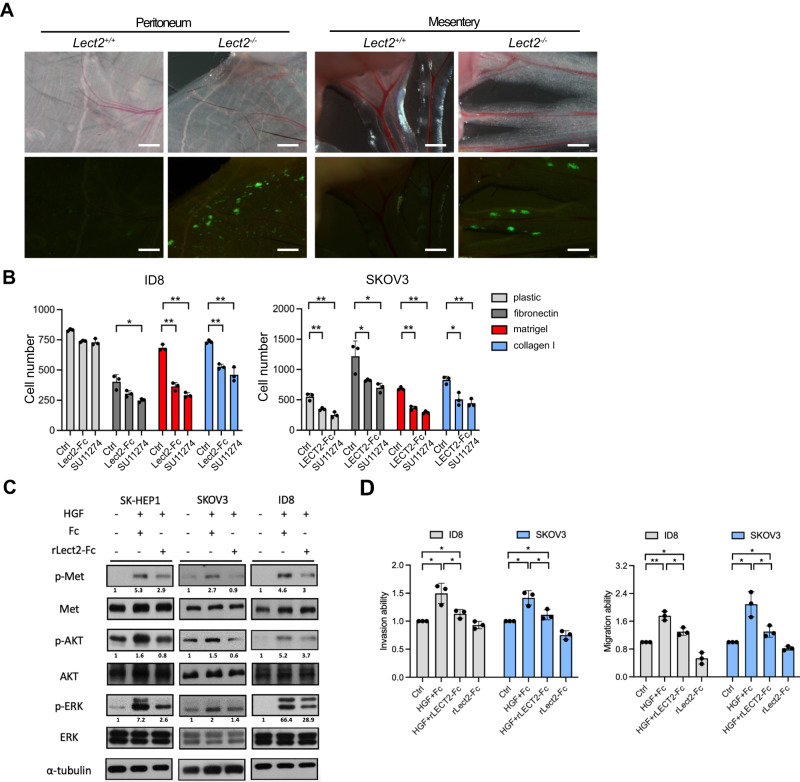
Fig. 3. Recombinant Lect2 protein suppresses the HGF/c-Met signaling axis in ovarian cancer cells.
A The in vivo adhesion abilities of CMFDA-labeled ID8 cells in the peritoneum and mesentery were dissected from mice 24 h after injection. Scale bar, 500 μm. B CMFDA-labeled cells were treated with recombinant LECT2/Lect2 proteins (200 ng/ml) or SU11274 (Met inhibitor, 10 nM). After incubation for 1 h at 37°C, attached cells were counted. C Western blot analysis indicates that HGF (30 ng/ml) activates the c-Met tyrosine kinase pathway, while recombinant Lect2 (200 ng/ml) mitigates HGF/c-Met signaling. Western blot quantifications using ImageJ were marked below the indicated molecules. D The suppression ability of recombinant LECT2/Lect2 proteins in the transwell migration and invasion assays of HGF-induced SKOV-3 and ID8 cells. HGF (30 ng/ml), recombinant LECT2/Lect2 (200 ng/ml), and Fc (200 ng/ml) were used as indicated. In (C) & (D), human and mouse recombinant LECT2/Lect2 were used for the human and mouse cell lines, respectively. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.