FIGURE 3.
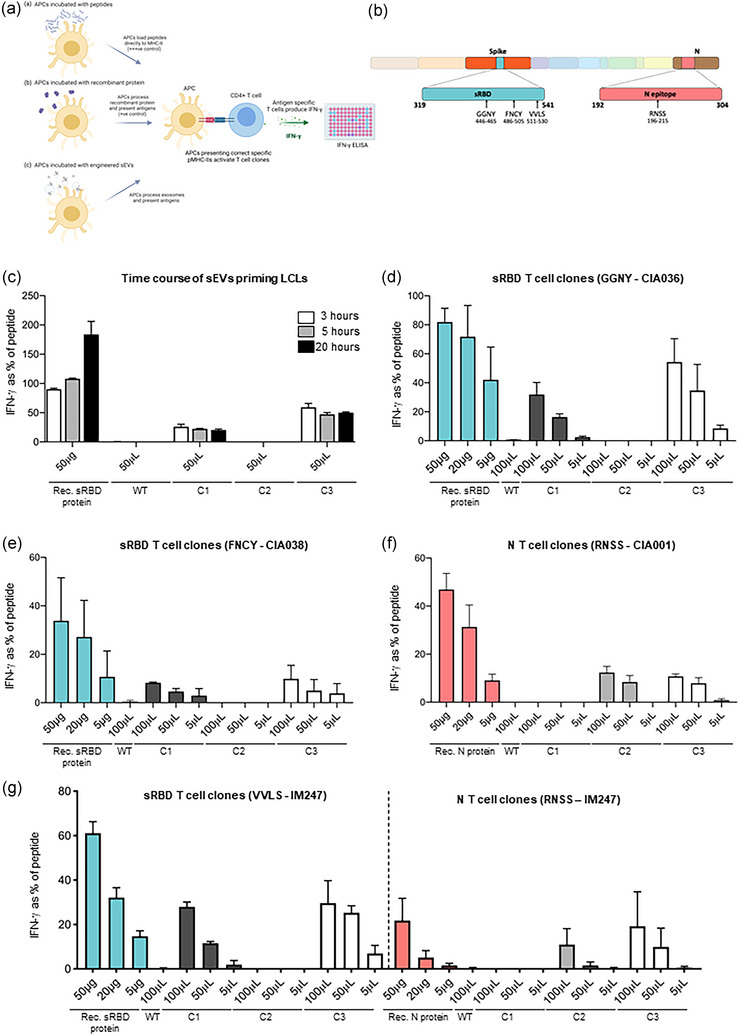
APCs primed with engineered sEVs can elicit recognition by T cell clones. (a) A schematic representation of the T cell assays utilised. B cell‐derived lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) expressing relevant HLA class II restriction alleles were established as antigen presenting cells (APC). These were exposed to either pepmix (+++ ’ve control), recombinant sRBD or N protein (+’ve control) or purified sEVs, then washed and co‐cultured with T cell clones. After 18 h of co‐culture, the culture supernatant medium was harvested and the IFN‐γ release into the supernatant was tested by IFN‐γ ELISA. (b) Schematic representation of the domains in the SARS‐CoV‐2 genome organization. The regions included in our genetically engineered sEVs; sRBD (residues 319–541 of SARS‐CoV‐2 Spike) and an antigenic fragment of nucleocapsid (N) protein (residues 192–304), are highlighted. The epitopes recognized by the T‐cell clones specific for sRBD (GGNY, FNCY and VVLS) and N (RNSS) are also highlighted. (c) LCLs were incubated with peptide, recombinant sRBD protein or 100 μL sEVs for either 3, 5 or 20 h. LCLs were then washed before being co‐cultured with sRBD‐specific (epitope GGNY) T cell clones. IFN‐γ release was measured by ELISA and values normalised against the mean maximal response detected against the epitope peptide. n = 2; mean ± SEM. (D‐G) LCLs were treated as described for panel C, but for 3 h only, were washed and co‐cultured for 18 h with T cell clones specific for the following epitopes: (d) sRBD epitope GGNY, (e) sRBD epitope FNCY, (f) N epitope RNSS. (g) LCL IM247, which expresses the HLA class II restriction alleles for the sRBD epitope VVLS and the N epitope RNSS was incubated as described in panel C. After washing, the cells were co‐cultured for 18 h with either of the two T‐cell clones, quantifying the display of both epitopes from the same LCL. For panels C‐G, n = 3; mean ± SEM. Rec. protein: recombinant protein.
