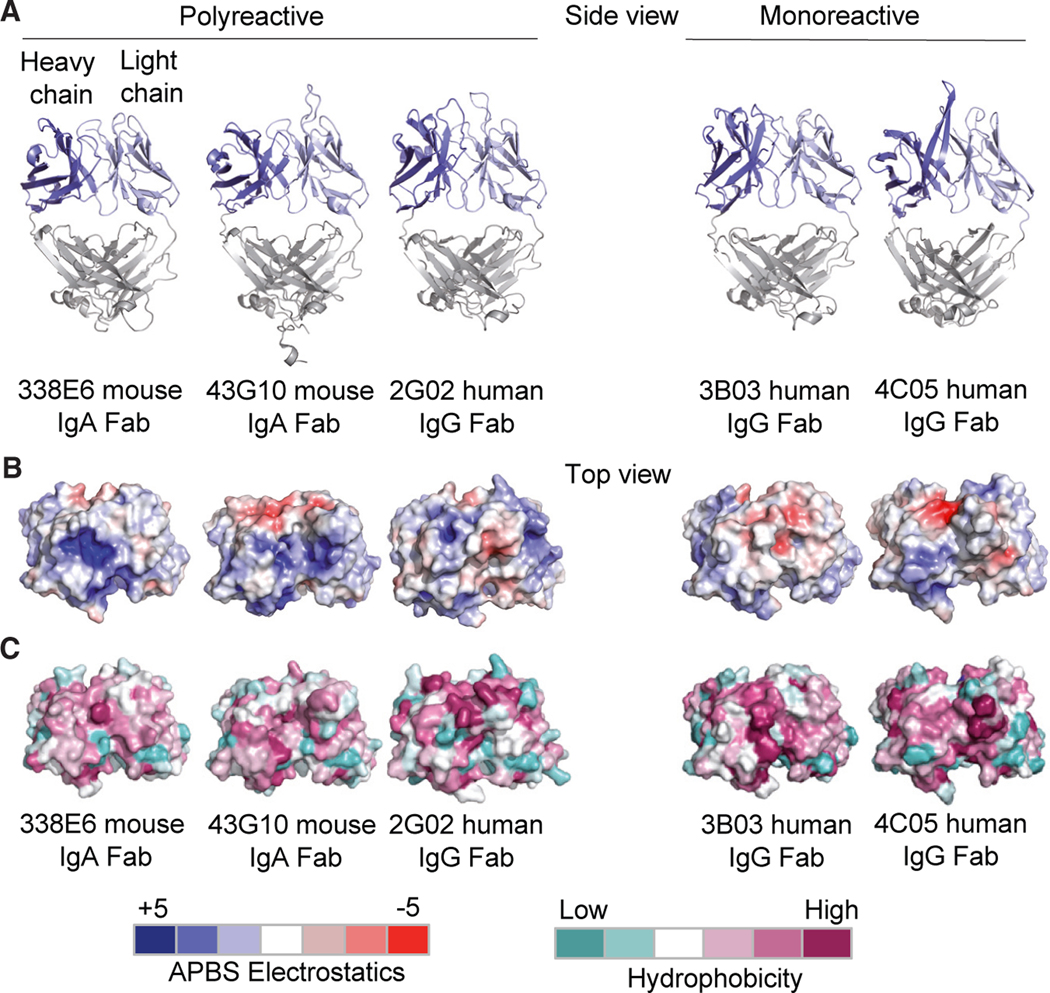
Figure 3. Structural features of polyreactive and monoreactive Fabs.
(A) Side view of crystal structures of the polyreactive mouse 338E6 (PDB: 8FZO), mouse 43G10 (PDB: 8FZP), human 2G02 (PDB: 8G1B), and monoreactive human 3B03 (PDB: 8G1C) and human 4C05 (PDB: 8G19) Fabs, shown in cartoon representation. The variable heavy-chain (VH) and variable light-chain (VL) domains are colored in dark blue and light blue respectively.
(B and C) (B) Top view of surface representations of these five Fab structures highlighting Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver (APBS) electrostatics of their antigen-binding site with positive charges in scaled blue and negative charges in scaled red (APBS scale shown at bottom of figure). (C) Top view of surface representations of the antigen-binding regions (including the CDR loops) of these five Fab structures highlighting Eisenberg scale of hydrophobicity with low hydrophobicity shown in scaled teal and high hydrophobicity in scaled mauve (hydrophobicity scale at bottom of figure).