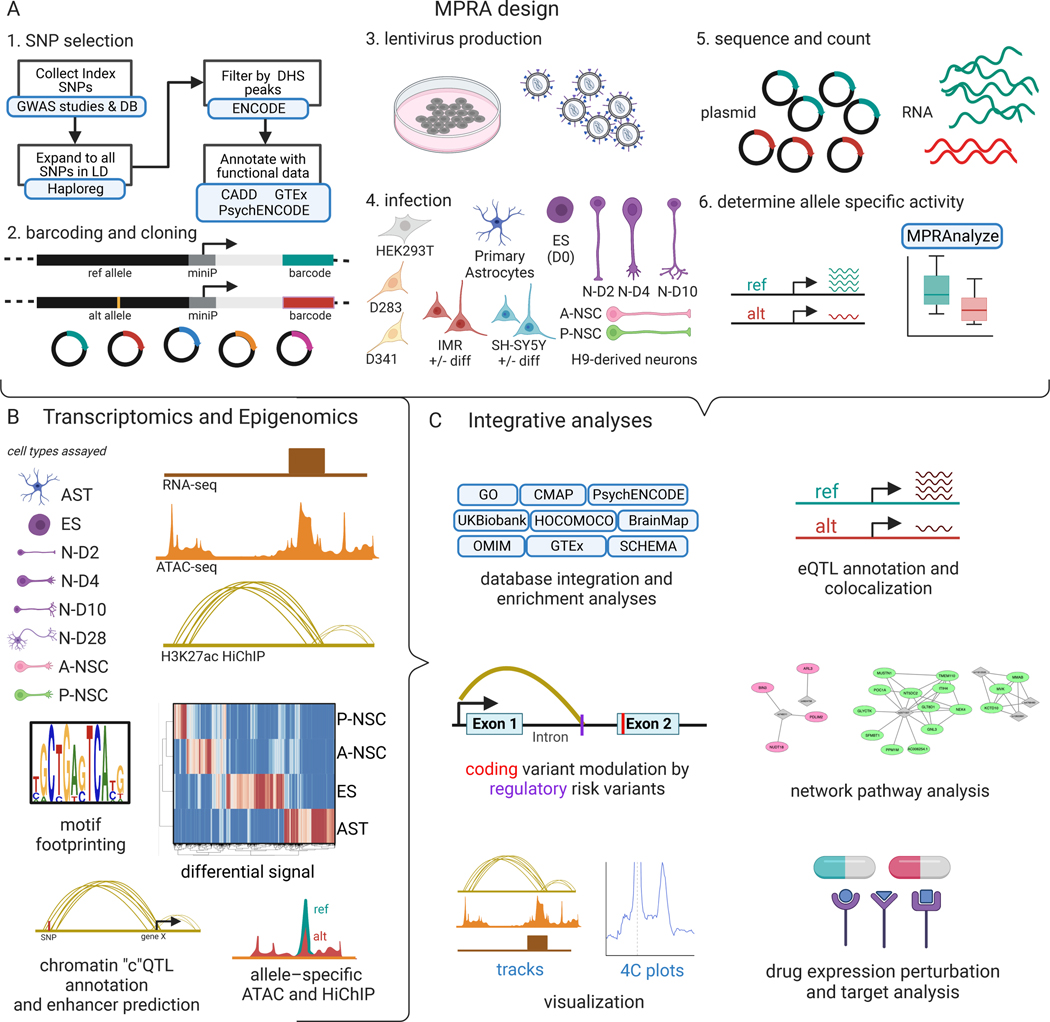
Fig. 1. MPRA, transcriptomic, and epigenomic integrative analyses for neuropsychiatric disorders.
(A) Schematic depicting lentiviral MPRA design for uncovering allelic specific activity. 250bp oligos were designed to assay 2221 neuropsychiatric disease GWAS loci. SNVs were selected from GWAS studies then filtered through publicly available epigenomics and eQTL datasets. H9 human ES cells, H9-derived neurons on days 2, 4 and 10 of differentiation (N-D2, N-D4, N-D10), anterior and posterior neural stem cells (A-NSC and P-NSC, respectively), astrocytes (AST), and cell lines (HEK293Ts, D283, D341, IMR-32 cells (+/− differentiation), and SH-SY5Y (+/− differentiation) were infected with the lentiviral MPRA library. (B) Schematic indicating the cell types in which RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, and HiChIP were performed as well as subsequent assay-specific analysis. Heatmap shows differential RNA-seq expression. (C) Analyses that integrate MPRA, transcriptomic, and epigenomic data to explore transcription regulatory pathomechanisms.