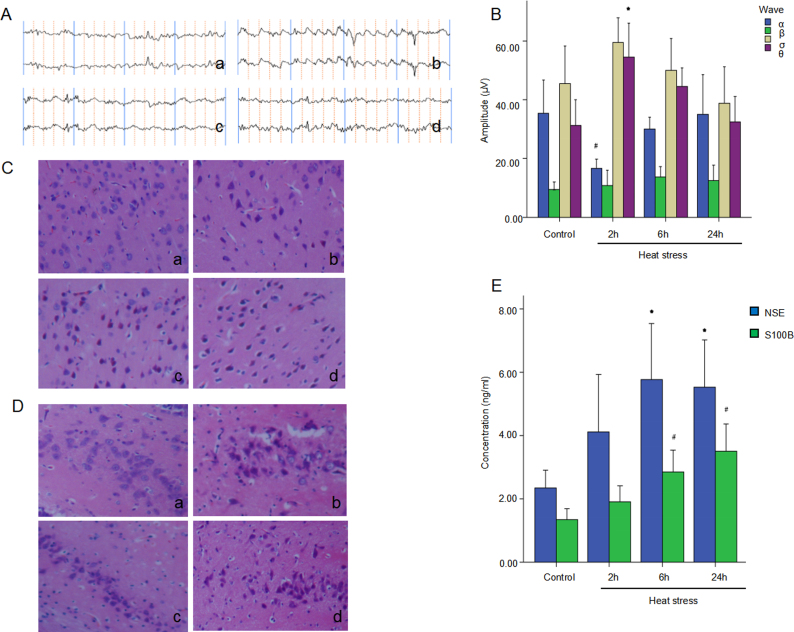
Fig. 1.
Heatstroke induces brain injury in rats. Male Wistar rats were subject to heat stress, and the rats were then cooled at an ambient temperature of (25 ± 0.5) °C for 2, 6, 24 h after the Tc reached 41 °C. Rats in the control group were maintained at (25 ± 0.5) °C and a humidity of 35% ± 5%. (A & B) EEG waves and corresponding quantifications of 4 waves were calculated and shown. ∗p < 0.05 vs. control group, #p < 0.05 vs. control group. (C & D) HE staining of cerebral cortex and hippocampus are shown, respectively. (E) The levels of Serum NSE and S100B in each group are shown. ∗p < 0.05 vs. control group, #p < 0.05 vs. control group.
Tc: core temperature; EEG: electroencephalogram; HE: hematoxylin-eosin; NSE: neuron-specific enolase.