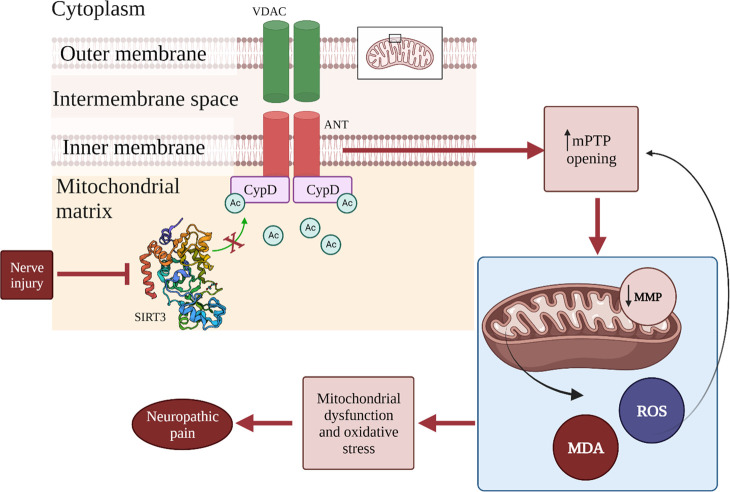
Figure 6.
Role of SIRT3 in the development of neuropathic pain. Nerve injury leads to the loss of SIRT3 deacetylase activity on CypD. The red arrows show the consequences of this: increased opening of mPTP, decreased MMP, release of ROS, and MDA. The increase of ROS levels also leads to an augmented opening of mPTP. This contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress and, finally, participates in the development of neuropathic pain. Adapted with permission from ref (152). Copyright 2022 Hindawi.