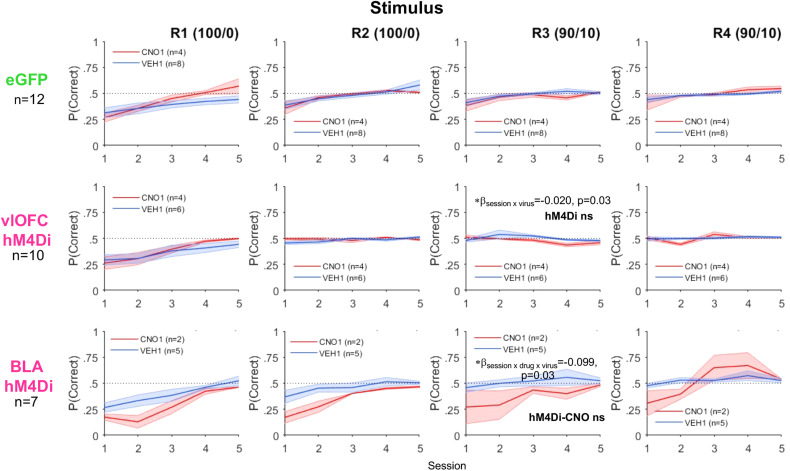
Figure 7.
BLA inhibition further slows incremental stimulus-based reversal learning whereas vlOFC inhibition abolishes learning after first reversal. Accuracy in stimulus learners measured by mean probability correct for the first five sessions of each deterministic (100/0) and probabilistic (90/10) reversal. Drug order was counterbalanced such that on R2 and R4 animals received VEH if they were administered CNO first on R1 and R3 and vice versa. Despite animals reaching the criterion on initial learning (Fig. 2C), animals exhibited poor stimulus-based reversal learning. Reversal learning was particularly flat for R3 (first probabilistic reversal) following vlOFC inhibition compared to eGFP. Reversal learning across all reversals was especially slow for animals following BLA inhibition. Bonferroni-corrected post hoc comparisons following a mixed-effect GLM wherein a session × virus interaction or a session × drug × virus was found resulting in *p < 0.05 effect of session in eGFP, but not in hM4Di or hM4Di-CNO.