Figure 2. Muscle immunocyte accumulation, oxidative phosphorylation, and interferon signaling are indued by endurance exercise training.
(A-F) 8-week-old mice were individually housed for 2–4 weeks with or without access to running wheels equipped with activity-tracking software. Hindlimb muscles were isolated for cytofluorometric (n≥5) and transcriptomic (n=3) analyses after a 24h washout period.
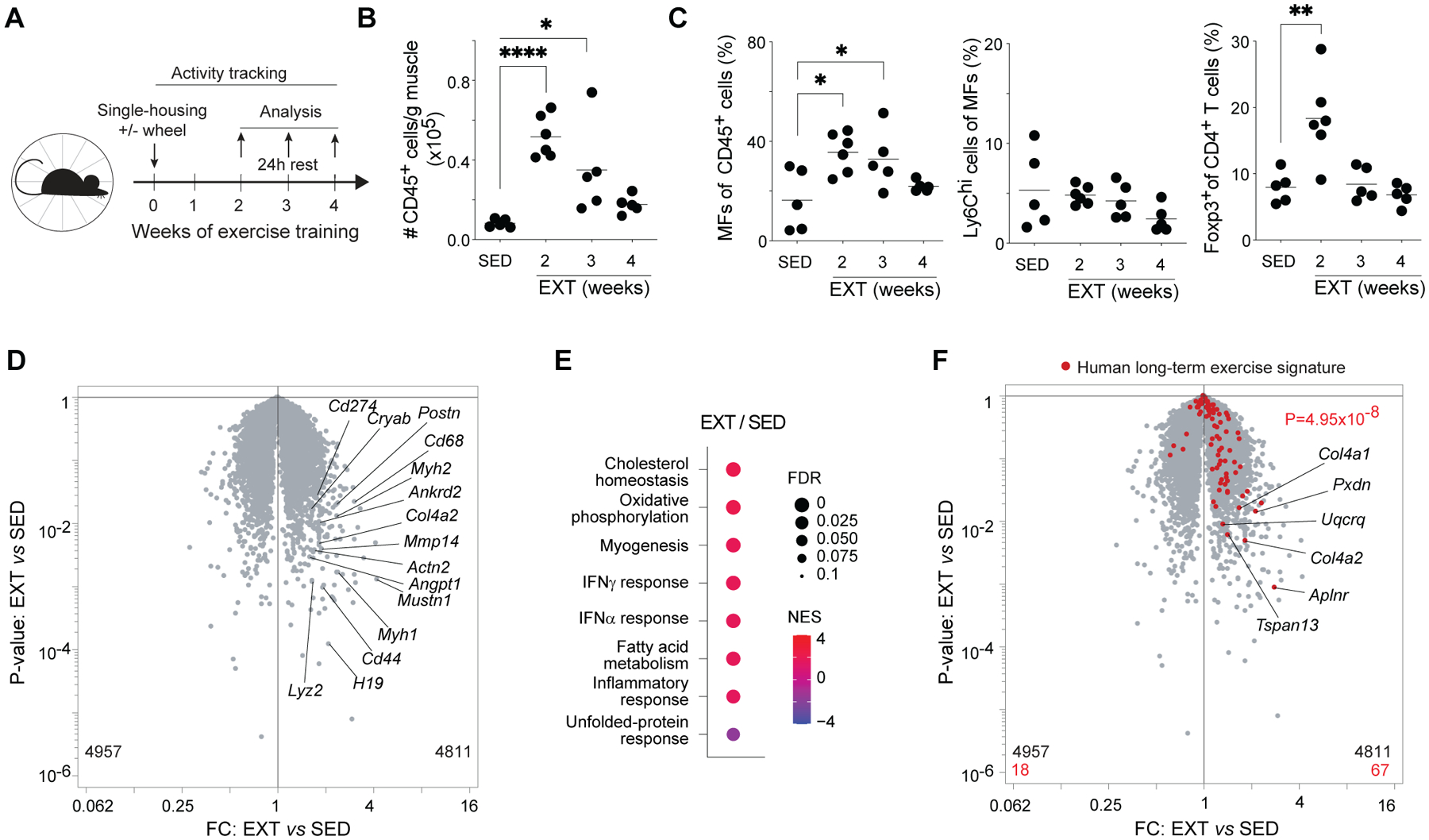
(A) Schema for EXT experiments.
(B) Number of immunocytes per gram of muscle.
(C) Frequencies of MFs, Ly6Chi MFs, and Tregs.
(D) RNA-seq analysis of Qd muscles from sedentary and 2-week exercise-trained mice.
(E) GSEA showing top Hallmark gene sets enriched or impoverished in Qd muscles after 2wk EXT.
(F) Volcano plot overlain with genes differentially enriched in human muscles after long-term exercise (21).
Summary plots show data pooled from ≥2 independent experiments.
*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test comparing each week of EXT to sedentary controls (B and C) or p value computed by the χ2 test (F). EXT, exercise training; FC, fold-change; FDR, false-discovery rate; NES, normalized enrichment score; all other abbreviations as per prior figures.
