FIG 2.
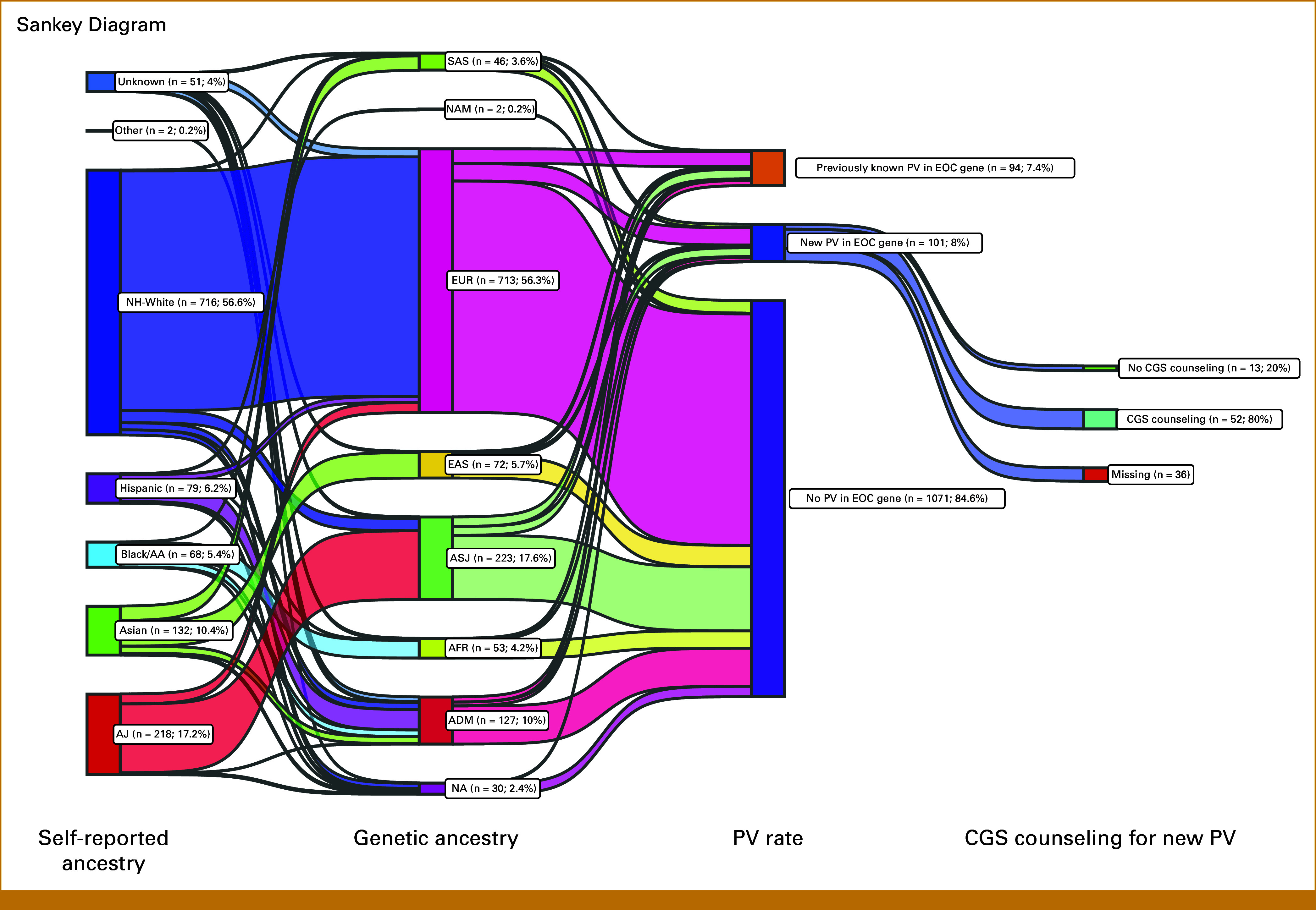
Sankey diagram depicting self-reported ancestry, genetic ancestry, presence of germline pathogenic variants, and clinical genetics counseling. Using self-reported ancestry, patients were classified into AJ, Asian, Black/AA, Hispanic, NH-White, other, and unknown groups. Use of genetic ancestry further classified patients into ADM, AFR, ASJ, EAS, EUR, NAM, and SAS groups. A small subset (2.4%) of patients were unable to be classified into a genetic ancestry category. The rate of newly diagnosed PV in an EOC-related gene was 8%, compared with 7.4% of patients who previously knew about their PV in an EOC-related gene. Of patients with a new PV finding in an EOC-related gene for whom we have CGS data available, 80% underwent CGS counseling. AA, African American; ADM, admixed; AFR, African; AJ, Ashkenazi Jewish; ASJ, AJ genetic ancestry; CGS, Clinical Genetics Service; EAS, East Asian; EOC, epithelial ovarian cancer; EUR, European; NA, not applicable; NAM, Native American; NH, non-Hispanic; PV, germline pathogenic/likely pathogenic variant; SAS, South Asian.
