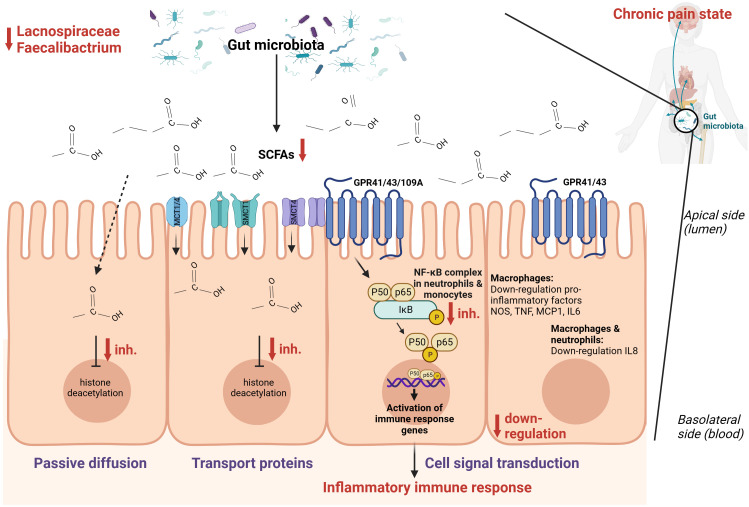
Figure 3.
Hypothesized schematic representation of the role of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the regulation of gut and systemic immunity in relation to chronic pain (86–88). SCFAs can regulate inflammation through cell signal transduction by binding at G-protein coupled receptors GPR109A, GPR43, and GPR41 and down-regulate the NOS, TNF, MCP-1, IL-6, IL-8, and the NF-κB signaling pathway. Through passive diffusion and transport proteins (MCT1, MCT4, SMCT1, SMCT2), SCFAs can inhibit histone deacetylase. This is a simplified representation of the pathways involved in inflammation with the pathways expected to be relevant in the setting of chronic pain.