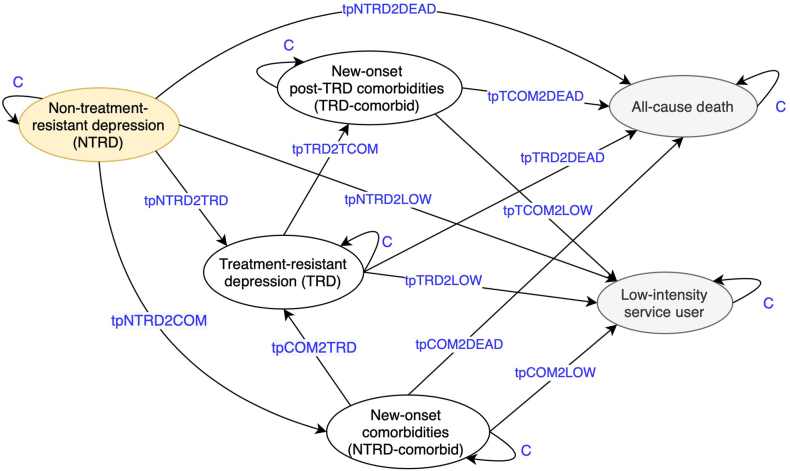
Fig. 1.
Schematic presentation of the Markov model structure. Yellow oval represents the initial state, grey ovals represent the absorbing states and blue texts represent the time-varying transition probabilities. “C” represents the complement of other probabilities from the same state. The definitions of the health states are as follows. Non-treatment-resistant depression (NTRD): Patients with depression who were yet to develop TRD or further clinical characteristics. Treatment-resistant depression (TRD): Patients who took at least two antidepressant regimens for an adequate duration and had the third regimen to confirm refractoriness in the first two regimens. New-onset comorbidities (NTRD-comorbid): Patients with new-onset somatic comorbidities included in the list of diseases used to calculate Charlson Comorbidity Index, or pre-specified psychiatric comorbidities before TRD, and the new-onset condition(s) did not occur before depression diagnosis. New-onset post-TRD comorbidities (TRD-comorbid): Similar to NTRD-comorbid but condition(s) occurred only after TRD. Low-intensity service user (absorbing state): Patients with minimal care need and free of further depression-related diagnosis records and antidepressant prescriptions. The health state acts as a proxy for recovery from depression, rather than relapse or recurrence manifested during the development of TRD. Patients in this state are not considered as active or living with depression. All-cause death (absorbing state): Observable deaths regardless of causes.