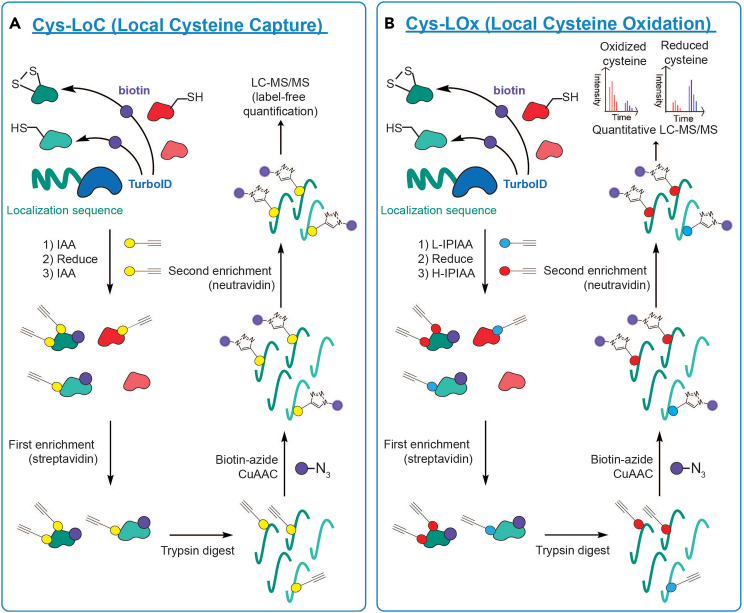
Figure 1.
Workflows for (A) Cys-LoC (Local Cysteine Capture) and (B) Cys-LOx (Local Cysteine Oxidation)
(A) A localized TurboID construct (e.g., mitochondria-localized) will biotinylate proteins within a single subcellular compartment, which are represented here as green-colored proteins. Cells are then lysed, and all natively reduced cysteines are labeled with iodoacetamide alkyne (IAA) prior to addition of DTT to reduce natively oxidized cysteines, as DTT can interfere with iodoacetamide labeling of cysteines. In order to ensure comprehensive profiling of localized cysteines, natively oxidized cysteines are then reduced and capped by a sequential round of IAA labeling (using an excess of IAA relative to DTT). Streptavidin enrichment then enriches biotinylated proteins from a single cellular compartment (e.g., mitochondria), and an on-resin trypsin digest releases peptides from the enriched proteins. IAA-labeled peptides are then conjugated to biotin-azide via CuAAC ‘click’ chemistry, and biotinylated peptides are enriched by neutravidin. Enriched peptides are then analyzed by label-free LC-MS/MS to identify cysteines from the specified subcellular location.
(B) A localized TurboID construct (e.g., mitochondria-localized) will biotinylate proteins within a single subcellular compartment. After cell lysis, natively reduced cysteines are labeled with “light” isopropyl iodoacetamide alkyne (L-IPIAA). Natively oxidized cysteines are then reduced and capped by “heavy” isopropyl iodoacetamide alkyne (H-IPIAA), such that reduced and oxidized cysteines are differentially labeled. Streptavidin enrichment then enriches biotinylated proteins from a single cellular compartment (e.g., mitochondria), and an on-resin trypsin digest releases peptides from the enriched proteins. IPIAA-labeled peptides are then conjugated to biotin-azide via CuAAC ‘click’ chemistry, and biotinylated peptides enriched by neutravidin. Enriched peptides are then analyzed by quantitative LC-MS/MS to quantify redox states of the cysteines from the specified subcellular location.