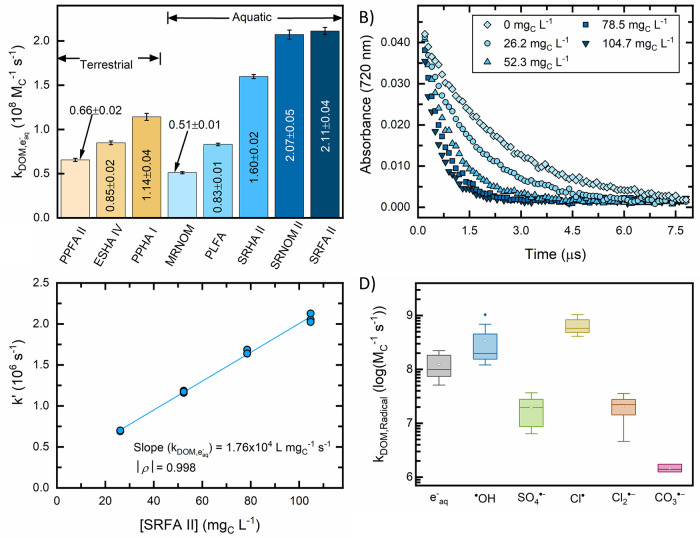
Figure 1.
Bimolecular rate constant measurements between eaq– and DOM isolates (kDOM,e–aq). Isolates include Elliott Soil IV humic acid (ESHA IV), Pahokee Peat II fulvic acid (PPFA II), Pahokee Peat I humic acid (PPHA I), Upper Mississippi River natural organic matter (MRNOM), Pony Lake fulvic acid (PLFA), Suwannee River II humic acid (SRHA II), Suwannee River II natural organic matter (SRNOM II), and Suwannee River II fulvic acid (SRFA II). kDOM,e–aq in (A) were determined by measuring (B) transient absorption decay kinetics of eaq– at 720 nm for various [DOM] and plotting (C) pseudo-first-order rate constant as a function of [DOM]. (B, C) Data for SRFA II only. The solid line in (C) represents a linear fit to the data using the least squares method with the slope reported as the kDOM,e–aq. Similar (C) plots for other DOM isolates are found in SI Figure S1. Error bars in (A) represent the standard error of the slope in (C). kDOM,e–aq were compared to bimolecular rate constants between other radicals7−11 and DOM isolates in (D). DOM-eaq– experiments conducted at pH 7.0 ± 0.1, 22 ± 2 °C, and 10.0 mM phosphate buffer. All other radical experiments in (D) were conducted at pH 7.0, room temperature, and varying concentrations of phosphate buffer.