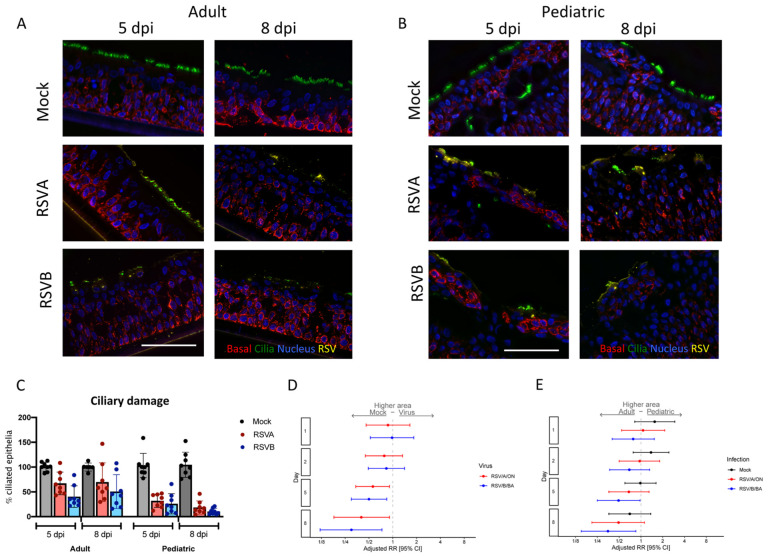
Figure 4. Ciliary damage in pediatric and adult HNO-ALIs.
A) Representative IF imaging of a single adult HNO at 5 and 8 days post-infection (dpi). Basal cells are stained in red by Krt5, ciliated cells are stained in green by acetylated alpha tubulin, RSV particles are stained in yellow by anti-RSV antibody, and cellular nuclei are stained in blue by DAPI and B) single pediatric HNO-ALI at 5 and 8 dpi. Basal cells are stained in red by Krt5, ciliated cells are stained in green by acetylated alpha tubulin, RSV particles are stained in yellow by anti-RSV antibody, and cellular nuclei are stained in blue by DAPI. Scale bar is 100 μm. C) Percentage of ciliary damage in adult vs pediatric HNO-ALIs at 5 or 8 dpi. In this graph, the ciliary area is normalized to the corresponding HNO-ALI mock infection being 100%. D) Forest plot of mock versus virus of cilia area modeled on the following factors: the interaction of dpi and age, the interaction of age and viral infection, and the interaction of dpi and virus. Adjusted risk ratio estimates and their associated 95% confidence intervals are represented by dots and T-bars, respectively. E) Forest plot of ciliary area of adults versus pediatrics was modeled on the following factors: the interaction of dpi and HNO-ALI age, the interaction of age and viral infection, and the interaction of dpi and virus. Adjusted risk ratio estimates and their associated 95% confidence intervals are represented by dots and T-bars, respectively.