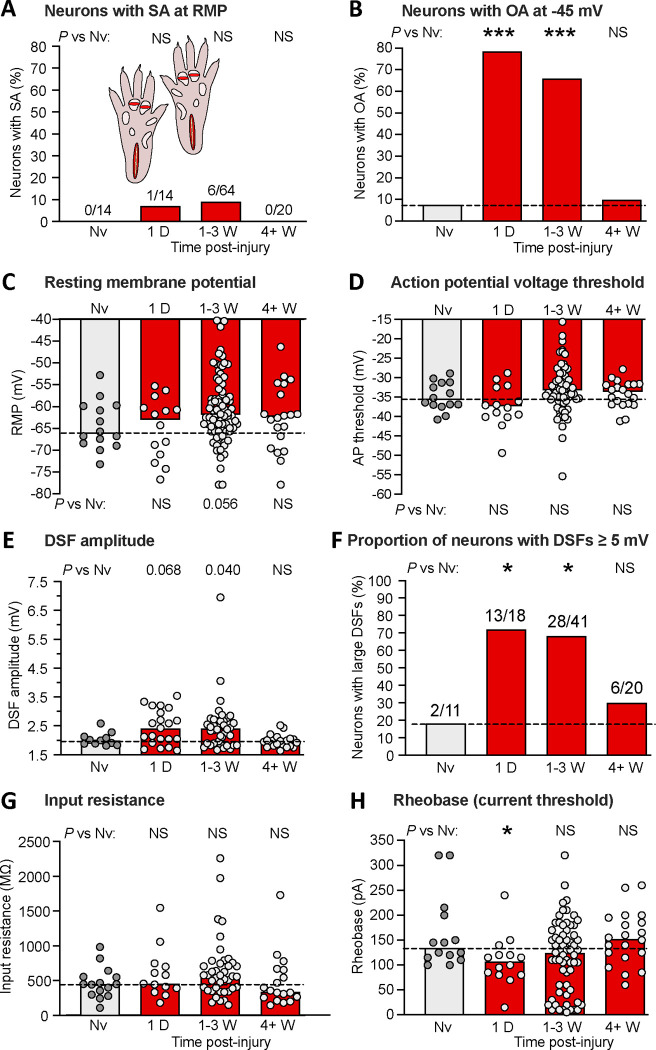
Figure 5.
Bilateral extended plantar incision (EPI) induces long-lasting hyperexcitability that is retained after dissociation of DRG neurons. (A) Proportion of neurons exhibiting SA (OA at RMP) when dissociated at the indicated number of postinjury days or weeks following bilateral EPI. Above each bar are the number of neurons exhibiting SA/the number of neurons sampled for that group. Comparisons of EPI with the naïve group at each time period were made with Bonferroni-corrected Fisher’s exact tests. (B) Proportion of the same neurons as in panel A that exhibited OA at −45 mV, assessed with Bonferroni-corrected Fisher’s exact tests. (C) Lack of significant alterations in RMP. Bars and dashed line (naïve group) represent medians. Comparisons by Mann-Whitney U tests with Bonferroni corrections for each time period versus naïve group. (D) Lack of significant alterations in AP voltage threshold as indicated by Mann-Whitney U tests with Bonferroni corrections. (E) Lack of significant alterations in DSF amplitudes (with a possible trend for enhancement). Comparisons were made at each time period versus naïve group with Mann-Whitney U tests with Bonferroni corrections. (F) Alterations in the proportion of DRG neurons exhibiting large DSFs (≥ 5 mV). Comparisons for each time period versus naïve group were made with Fisher’s exact tests. (G) Lack of alterations in input resistance, as assessed wiith Mann-Whitney U tests with Bonferroni corrections. (H) Alterations in rheobase (AP current threshold) assessed for each time period versus naïve group by Mann-Whitney U tests with Bonferroni corrections. AP, action potential; D, day; DSF, depolarizing spontaneous fluctuation; Nv, naïve; NS, not significant; W, weeks.