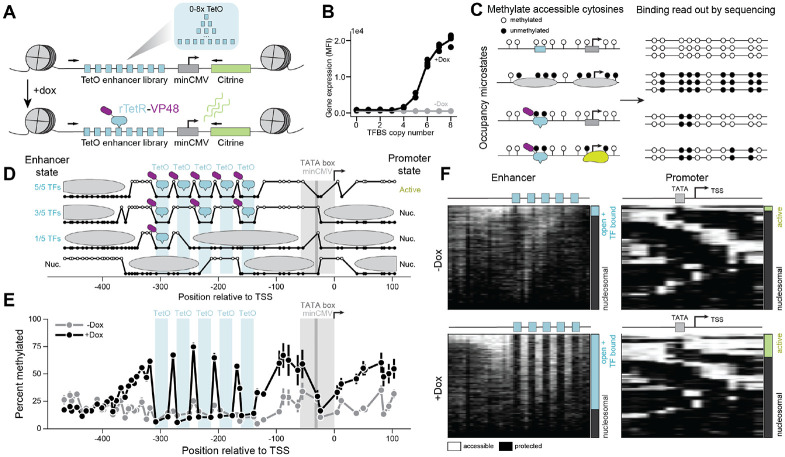
Figure 1: Single-molecule footprinting reveals TF occupancy and promoter state at an engineered, genome-integrated expression reporter system.
A) Variable numbers (0-8) of TetO binding sites (blue) upstream of a minCMV (gray) promoter and Citrine (green) gene were engineered into the AAVS1 locus in K562 cells expressing rTetR-VP48. Binding of rTetR-VP48 is inducible upon addition of doxycycline (dox) to cell media. Black arrows are the primers used to sequence the reporter.
B) Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of the Citrine reporter measured using flow cytometry after 24 hours of 1,000 ng/ml doxycycline exposure (black) as a function of the number of transcription factor TetO binding sites (TFBS).
C) Schematic describing the single-molecule footprinting (SMF) assay for determining the molecular state of regulatory elements or promoters. Accessible GpCs are methylated (white circles) while inaccessible GpCs remain unmethylated (black circles).
D) Example SMF molecules with 5 TetO sites, along with the molecular configuration interpretations for these molecules. The high state represents a methylated, accessible GpC, while a low state represents an unmethylated, inaccessible GpC.
E) Aggregated data obtained for the construct with 5 TetO sites present, with (black) and without (gray) dox present. Error bars represent standard error of the mean from 4 biological replicates.
F) Summary plots of single molecules (individual rows) observed by SMF for enhancers (left) and promoters (right) of constructs with 5 TetO sites without (top) and with (bottom) dox induction. Each GpC spans an equal width in this representation; methylated (accessible) Cs in white and unmethylated (protected) Cs in black. The bars at the right of each summary plot show the fraction of enhancer sites with one or more TF bound (open + TF bound; blue) or fully nucleosomal (gray) and the fraction of promoters that are not bound by a nucleosome (active; green) or bound by a nucleosome (gray).