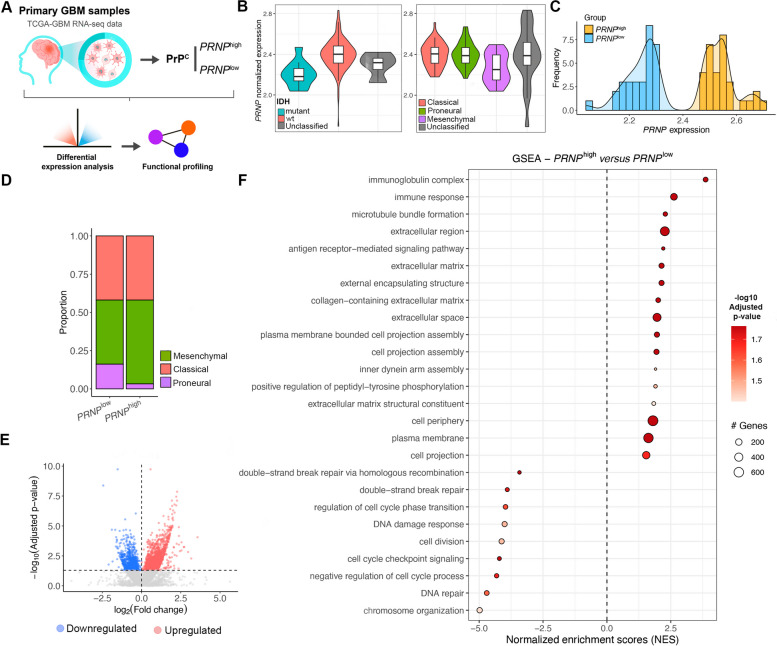
Fig. 1.
Impact of PRNP expression at bulk resolution in GBM samples from TCGA. A Schematic workflow of bulk RNA-seq data analyses of patient-derived primary GBM samples from TCGA (n=157). B Violin plots of PRNP normalized expression, according to log10 (counts per million [CPM]+1), in samples classified as IDH-mutant (n=11), IDHwt (n=142), or unclassified (n=4) (left, p=0.00016); and samples classified as classical (n=50), mesenchymal (n=67), proneural (n=18), or unclassified (n=22) (right, p=0.01). Kruskal-Wallis test. C GBM samples (n=124, after filtering) were ranked according to quartiles of PRNP expression. Those below the lower (PRNPlow, n=31) and above the upper quartile (PRNPhigh, n=31) were selected, as shown in the density plot of PRNP expression. D GBM molecular subtype composition of the PRNPlow and PRNPhigh groups. E Volcano plot of upregulated (red) and downregulated (blue) transcripts in PRNPhigh relative to PRNPlow. (The PRNP was removed from the plot). F Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) show enriched terms (Gene Ontology, GO) in the upregulated and downregulated transcripts of PRNPhigh GBM, sorted by normalized enrichment score (NES) and colored by adjusted p-value