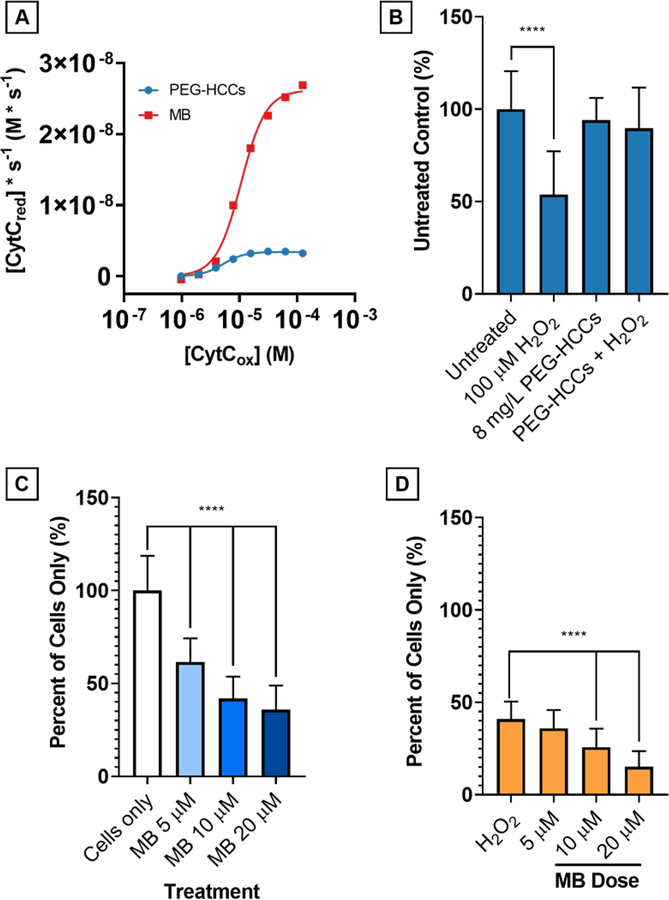
Figure 9.
Comparison of PEG-HCCs and MB at 4 mg/L concentration on reduction of CytCox by NADH (500 μM). A) On a mass concentration basis, MB has a higher Vmax than PEG-HCCs by nearly one order of magnitude. Without NADH, neither PEG-HCCs nor MB reduce CytC. PEG-HCCs rescue bEnd.3 cells from H2O2toxicity while MB is intrinsically toxic. B) bEnd.3 cells were treated with 100 μM H2O2 (54%, p < 0.0001) and 8 mg/L PEG-HCCs were added at 15 minutes following the initial insult. Live cell counts (n = 32) were performed and no toxicity of the PEG-HCCs (94%, p = 0.511) is observed, and 8 mg/L PEG-HCCs protection of bEnd.3 cells against H2O2 (90%, p = 0.105). C) MB given at 5, 10, and 20 μM causes dose-dependent cytotoxicity in bEnd.3 cells (p < 0.0001 at all levels). D) No protection is afforded when given immediately following treatment with 100 μM H2O2 (p < 0.0001 at all levels except 5 μM, p = 0.409).