FIG 3.
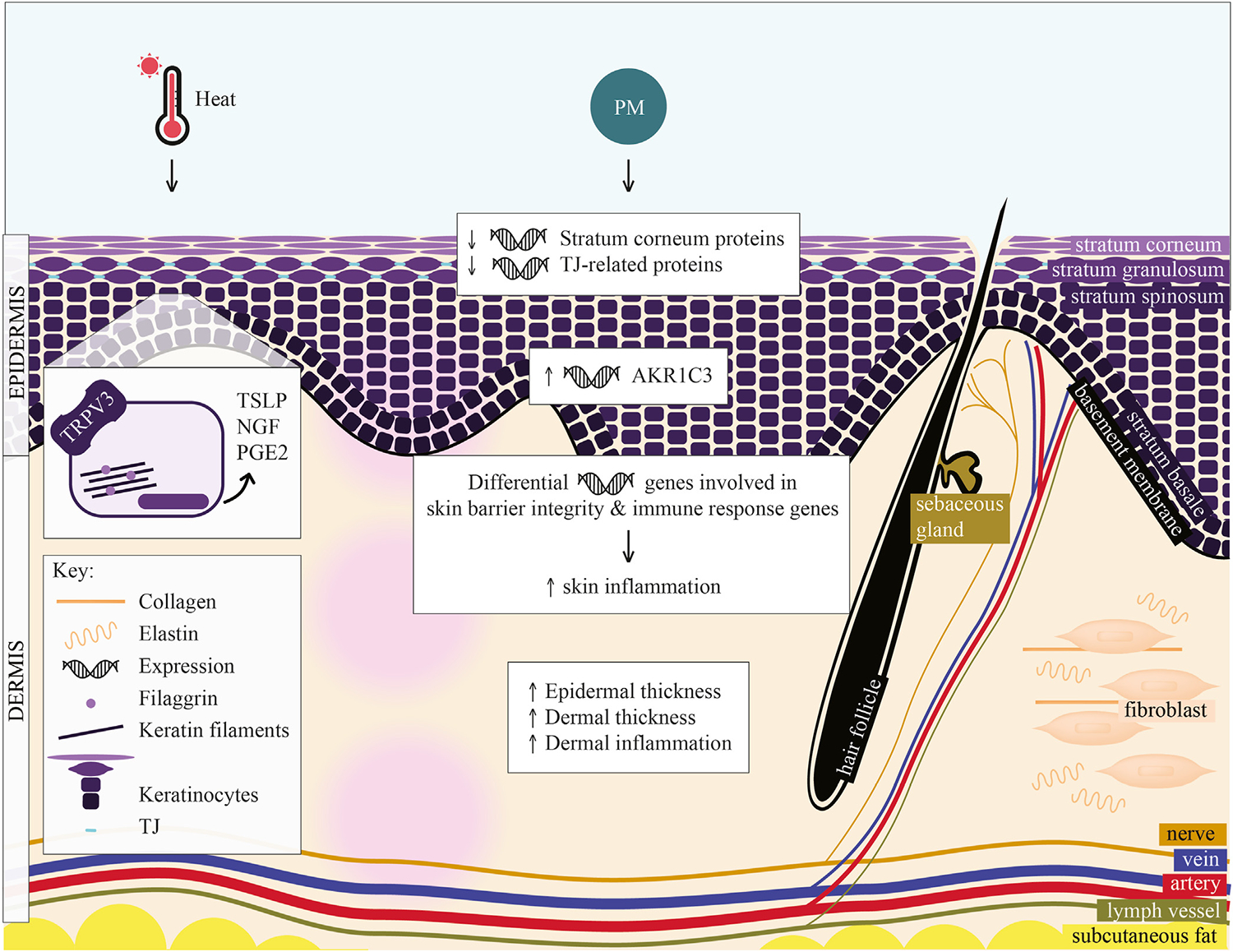
Hypothesized effects of heat and particulate matter on skin barrier structure. Skin is composed of epidermis and dermis; layers and components of these layers are labeled. Heat activates TRPV3 in keratinocytes, increasing TSLP, NGF, and PGE2. (TRPV3 expression and function is increased in AD.) PM has several hypothesized effects in AD: (1) decreases expression of stratum corneum and TJ-related proteins, (2) induces expression of AKR1C3 (AKR1C3 variant is overexpressed in AD), (3) leads to differential expression of genes controlling skin barrier integrity and immune response, increasing skin inflammation, and (4) results in increased epidermal and dermal thickness and increased dermal inflammation. NGF, Nerve growth factor; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin.
