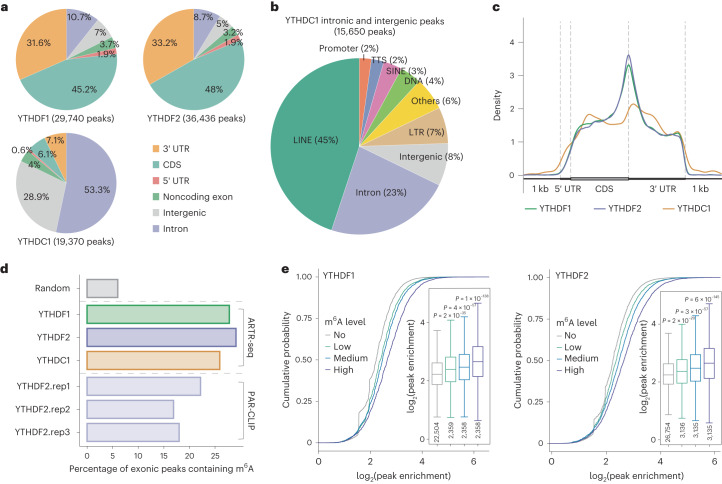
Fig. 5. ARTR-seq maps binding features of the selected m6A binding proteins.
a, Peaks distribution in 3′ UTR, CDS, 5′ UTR, noncoding exon, intergenic region and intron of YTHDF1, YTHDF2 and YTHDC1 identified by ARTR-seq for HeLa cells. b, A pie chart showing the detailed genomic feature distribution of YTHDC1 intronic and intergenic binding peaks. LINE, long interspersed nuclear elements. c, Aggregation profiles showing the meta distributions of binding peaks for YTHDF1 (green), YTHDF2 (purple) and YTHDC1 (orange) along mRNA transcripts. d, A bar plot showing the percentage of exonic peaks containing m6A sites detected by m6A-SAC-seq (ref. 33) for the m6A reader proteins. The random peaks are random exonic regions with the same lengths as pooled ARTR-seq peaks from the three reader proteins. Three replicates of published YTHDF2 PAR-CLIP data were used as the positive controls32. e, Cumulative curves and boxplots (inset) exhibit the log2 peak enrichment of ARTR-seq targets for YTHDF1 (left) and YTHDF2 (right). Peaks of m6A reader proteins were divided into four groups according to the modification fraction of the containing m6A (sum value) quantified by m6A-SAC-seq. The peaks without m6A were categorized in one group (No), and other peaks were divided into three groups with an equal number of peaks, including low m6A fraction (Low), medium m6A fraction (Medium) and high m6A fraction (High). The sample size was indicated below the respective box. P values were determined by the two-tailed Student’s t-test of indicated group versus the ‘no m6A’ group.