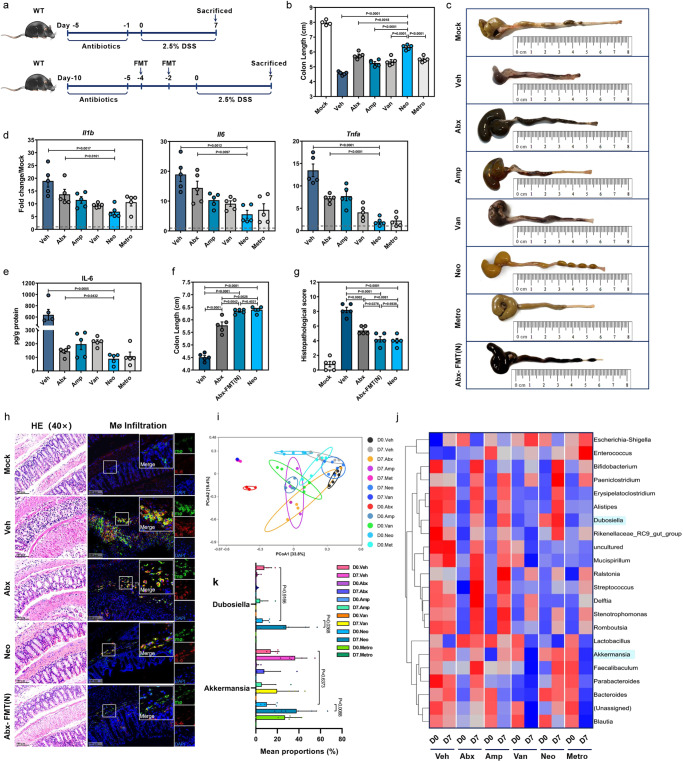
Fig. 1. Manipulation of gut microbiota affects mouse susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis.
a Outline of treatment regimens. b–e Wild-type C57BL/6J mice (WT, n = 4) received vehicle (Veh) or oral antibiotics (single Amp, Van, Neo, or Metro or in combination [Abx], n = 6) daily for 5 days and treated with 2.5% DSS in drinking water for 7 days. At day 7 (D7) post-DSS treatment, colon length (b, c), relative mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines Il1b, Il6, and Tnfa by qRT-PCR (d) and IL-6 protein level by ELISA (e) were determined in each group. f–h Abx mice were given fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from Neo-treated mice twice [Abx-FMT(N)] or Veh with a 48 h interval and then treated with DSS for 7 days (n = 5). WT B6 mice treated with Neo (Neo) were served as control. Colon length (f) was measured, histopathological changes were scored by HE staining (g, h) and infiltration of IL-6-secreting macrophages (Mø) was determined by IFA (h). i–j Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) (i) and heatmap of the relative abundance (j) of bacteria in fecal samples from mice treated with Abx or single antibiotics at D0 and D7 post-DSS administration. k Relative abundance of Dubosiella and Akkemansia at D0 and D7 among groups treated with different antibiotics (D7. Amp, D7. Van, n = 4; D0. Veh, D0. Abx, D0. Metro, D0. Amp. D0. Van, n = 5; D0. Neo, D7. Veh, D7. Neo, D7. Abx, D7. Metro, n = 6). Dashed lines at 1 indicate that the treatments have equal value as normalized controls. Results are representative of data generated in at least two independent experiments and are expressed as mean ± SEM, and 2-sided P-values were examined by the Student’s t-test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.