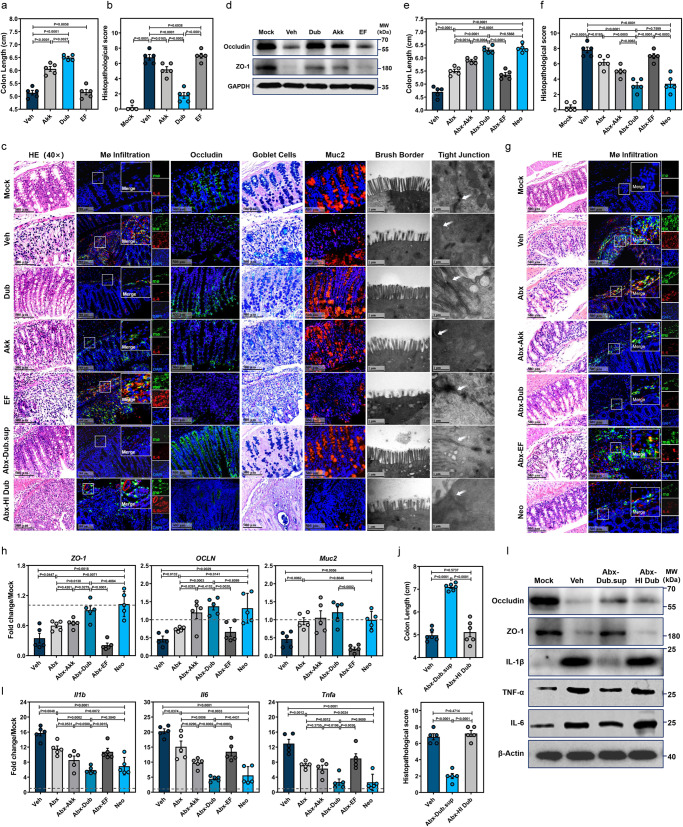
Fig. 2. D. newyorkensis protects mice from DSS-induced colitis and attenuates resulting mucosal inflammation and barrier damages.
a–d Conventional wild-type C57BL/6J mice were colonized with 109 CFU of D. newyorkensis (Dub), A. muciniphila (Akk), E. faecalis (EF) or vehicle (Veh) twice with 2-day break in between, then treated with DSS as previously described (n = 5). At D7 post-DSS administration, colon samples were collected to determine colon length (a), histopathological score (b) by HE staining, IL-6-secreting macrophage infiltration, Muc2 and Occludin expression by IFA, number of goblet cells by Alcian blue staining and microstructure of colonic epithelia by TEM (c). The expression of Occludin and ZO-1 in each group was determined by western blot (WB) (d). e–i Abx-treated WT mice were colonized with 109 CFU Dub, Akk, EF, or Veh and exposed to DSS (n = 5). At D7 post-DSS treatment, colon length (e), histopathological score by HE staining (f, g), IL-6-secreting macrophage infiltration (g) were examined. Meanwhile, the expression of ZO-1, OCLN, and Muc2 in isolated colonic intestinal epithelial cells (h), and the expression of proinflammatory cytokines Il1b, Il6, and Tnfa in colonic lamina propria (cLP) (i) was detected by qRT-PCR. c, j–l Conventional WT mice (n = 6) were orally administered heat-inactivated (HI) Dub, or Dub supernatant (Dub.sup) and exposed to DSS. At D7 post-DSS administration, colon length (j) was measured, histopathological changes were scored by HE staining (c, k, n = 5), level of tight junction proteins Occludin and ZO-1, and expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were determined by WB (l). Dashed lines at 1 indicate that the treatments have equal value as normalized controls. Results are representative of data generated in at least two independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± SEM, and 2-sided P-values were examined by the Student’s t-test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.