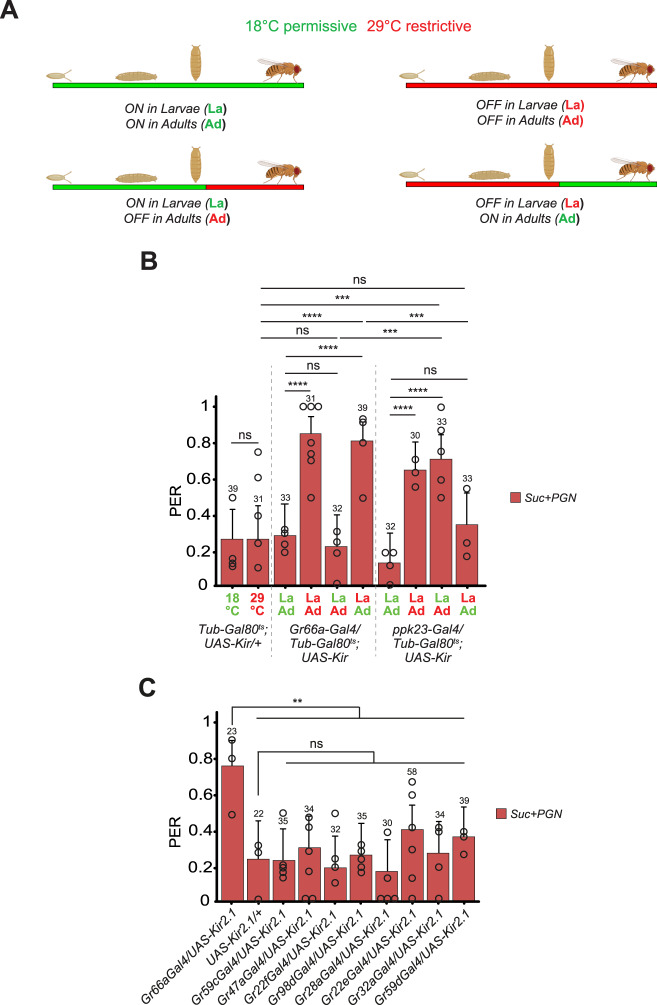
Fig. 3. Adult fly aversion to PGN requires functionally active larval Gr66A+ and adult ppk23+ neurons.
A Graphical representation of the life periods during which flies are shifted from 18 °C (green) to 29 °C (red). B Gr66a+ neurons are functionally required in the larval stage for PGN-triggered aversion, but are dispensable during adult life. In opposition to ppk23+ neurons which are required in the adult but not during the larval stages. PER index of flies to sucrose 1 mM + PGN from E. coli K12 at 200 µg/mL. The ubiquitously expressed Tub-Gal80ts, that inhibits the activity of Gal4, is temperature sensitive: it’s active at 18 °C and inactivated at 29 °C, allowing the expression of UAS-Kir2.1 and the consequent impairment of Gr66a+ or ppk23+ neurons activity. C Silencing of smaller subgroup of the Gr66a+ neurons population has no effect on the PGN-induced PER suppression. PER index of flies in which part of Gr66a+ neurons are inactivated via different Gr drivers guiding the expression of Kir2.1, to solutions of sucrose 1 mM + PGN from E. coli K12 at 200 µg/mL. For (B, C), PER index is calculated as the percentage of flies tested that responded with a PER to the stimulation ± 95% CI. The number of tested flies (n) is indicated on top of each bar. ns indicates p > 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01, *** indicates p < 0.001, **** indicates p < 0.0001 two-sided Fisher Exact Test. Further details including raw data and exact p-values can be found in the source data file.