Fig 2.
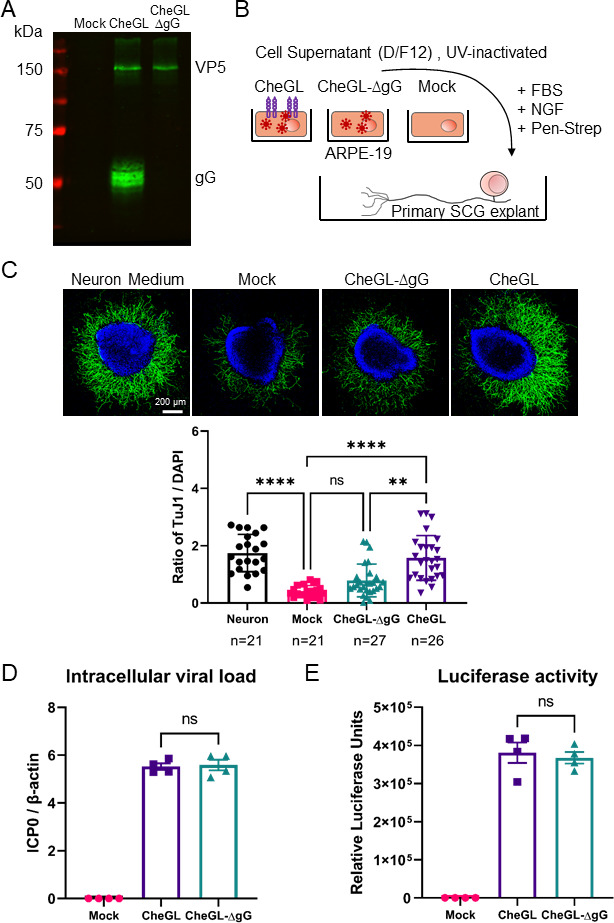
HSV1-CheGL, but not HSV1-CheGL-ΔgG, inhibits the repulsion of epithelial cells on neurite outgrowth. (A) Immunoblot detecting HSV-1 gG and major capsid protein VP5 in cell lysates of infected ARPE-19 cells. (B) Schematic representation of the neurite outgrowth assay. SCG from neonatal mice were seeded on collagen matrix and cultured with commercial neuron medium or conditioned medium from mock- or HSV-1-infected ARPE-19 cells supplemented with serum, NGF, and antibiotics. (C) The top panels show representative immunofluorescence confocal images of SCG incubated with neuronal medium or conditioned medium from mock- or HSV-1-infected ARPE-19 cells. The media were treated with ultraviolet light (UV) to inactivate HSV-1. After 20–24 hours, SCGs were fixed and labeled with anti-β-III-tubulin antibody (TuJ1, green) and stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 200 µm. The graph below shows the quantification of neurite outgrowth in each experimental group, presented as the ratio of neurite fluorescence intensity (TuJ1) to DAPI signal intensity for each SCG. Quantification was performed with FIJI software (see Materials and Methods). Each symbol corresponds to one SCG. N indicates the number of SCG in each experimental condition. (D) Graph showing intracellular viral genome copy numbers per cellular genome, detected by qPCR in DNA obtained from mock- and HSV-1-infected ARPE-19 cells at the time of supernatant collection (16 hours post-infection). HSV-1 genome copy number was quantified by amplifying ICP0, while the host genome was quantified by amplifying β-actin. Genome copy numbers were calculated by generating standard curves and presented as a ratio of ICP0 to β-actin. (E) Graph showing the amount of Gaussia luciferase detected in the supernatant of infected ARPE-19 cells at the time of supernatant collection (16 hpi). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation of the mean. Ns, not significant; ** P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 (Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test).
