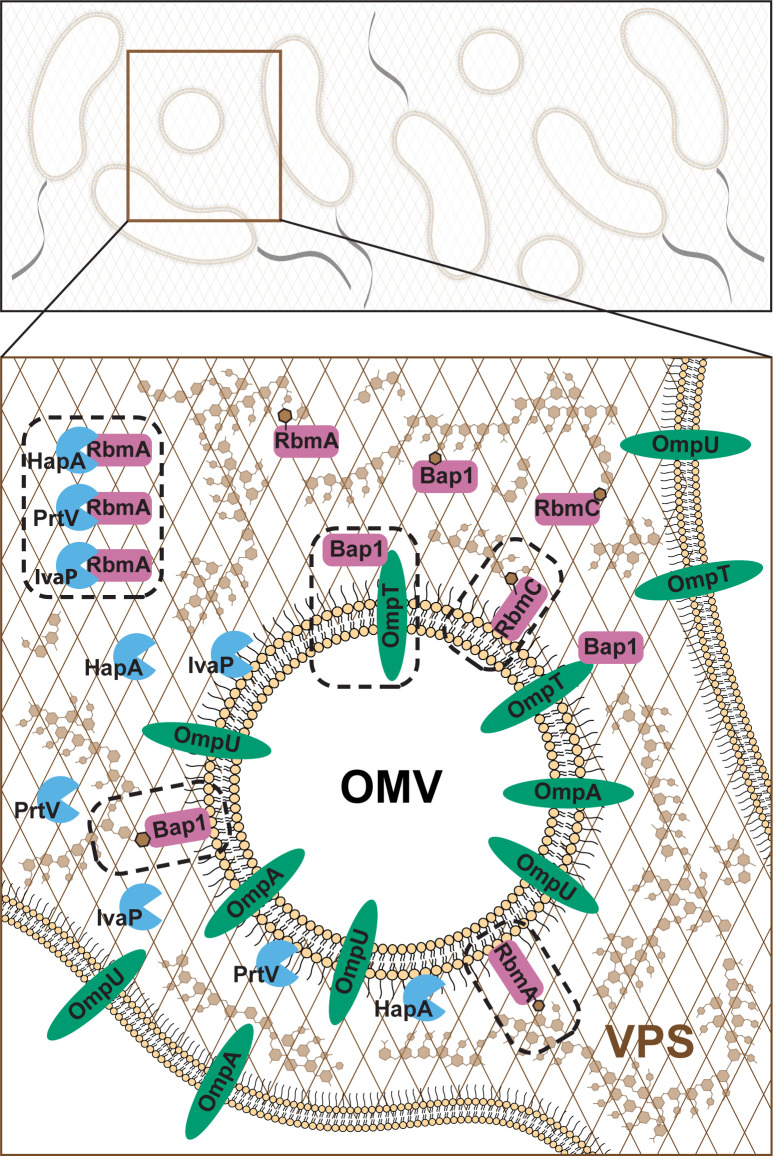
Fig 7.
Model of the role of OMVs in biofilm architecture. Biofilm formation and maintenance depend on producing extracellular matrix components—polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules. Matrix components are involved in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions and attachment to surfaces. A major component of the V. cholerae biofilm matrix is VPS, which is present throughout mature biofilms. VPS can interact with the biofilm matrix proteins RbmA, Bap1, and RbmC; these matrix proteins and VPS are OMV cargos. The proteases IvaP, PrtV, and HapA can all break down RbmA; these proteases are also OMV cargos. Thus, OMVs are likely to play a role in biofilm matrix assembly and matrix remodeling. Matrix proteins are shown in pink, extracellular proteases in blue, and OMPs in green. Dashed rectangles represent confirmed interactions. Figure is modified from Fig. 2 (4).