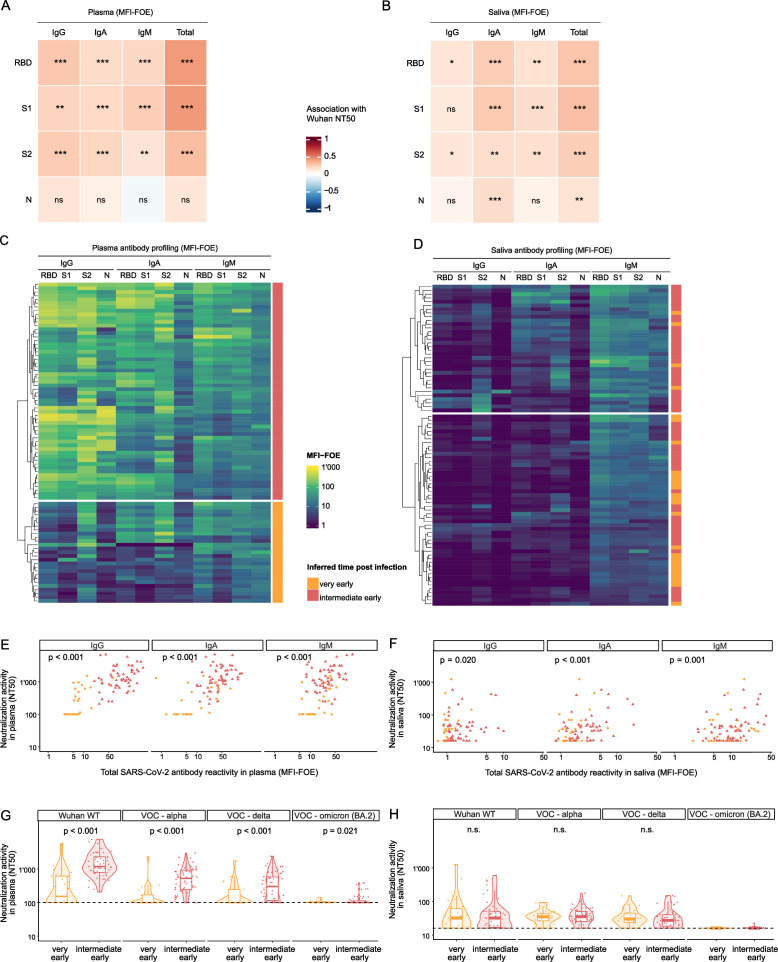
Fig 4.
Mucosal antibodies display broad neutralizing activity. (A and B) Heatmap of association coefficients between neutralization titers (NT50) against Wuhan-Hu-1 pseudotype and IgG, IgA, and IgM SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers in plasma (n = 85) (A) and saliva (n = 85) (B) obtained with tobit-regression analyses adjusted on age and sex to define association. Levels of significance are indicated as follows: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C and D) Heatmap representing MFI-FOE values of plasma (C) and saliva (D) samples of the cohort B2 (0–1 month, n = 85) and defining two subgroups of individuals: those very early after infection (no IgG response yet, orange, n = 27) and those intermediate early (IgG response detected, red, n = 58). (E and F) Association between neutralization titer (NT50) and total SARS-CoV-2 binding in plasma (E) and saliva (F) assessed in a tobit-regression model with all individuals grouped together (n = 85) and adjusted on age and sex. (G and H) Neutralization titers (NT50) against Wuhan-Hu-1 pseudotype, Alpha, Delta, and Omicron (BA.2) in plasma (G) and saliva (H) of individuals very early (orange circles, n = 27) and intermediate early (red triangles, n = 58) after infection. Dashed lines correspond to the limit of detection. P-values are obtained by comparing the two groups in tobit-regression models, adjusting for age and sex. Non-significant coefficients (P > 0.05) are marked “n.s.” No P-value was obtained for Omicron (BA.2) as most neutralization values are left-censored.