Figure 2.
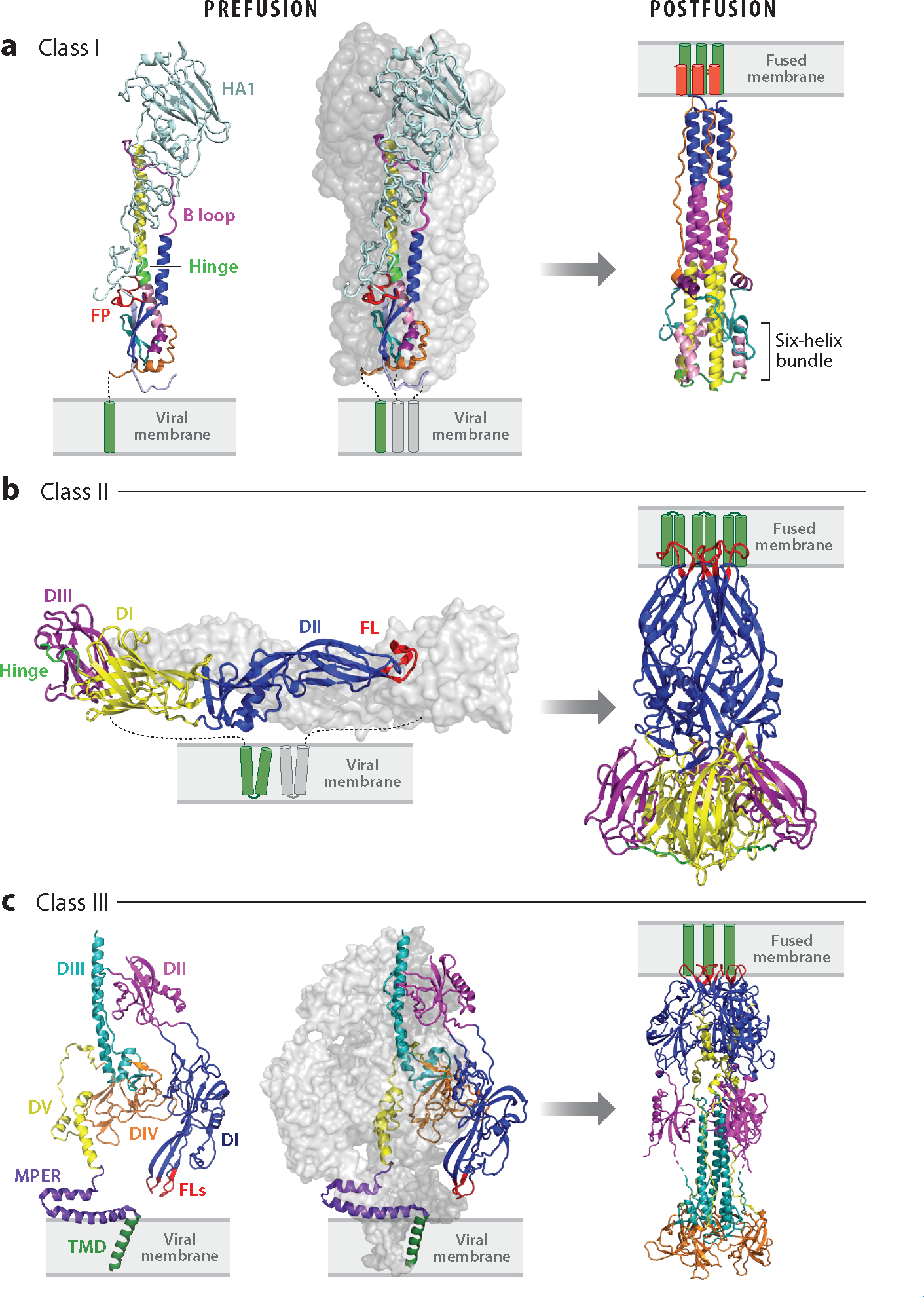
Pre- and postfusion structures of class I, II, and III viral fusion proteins. (a) Class I: influenza hemagglutinin (HA) in pre- [Protein Data Bank (PDB) 2HMG] and postfusion (PDB 1QU1) states (far left, excised prefusion monomer). The ectodomains of two monomers of the trimer are shown as surface representations in shades of gray; the other is colored: light blue, HA1; red, fusion peptide (FP); blue, helix A; magenta, B loop prefusion and helix B postfusion; yellow, helix C; neon green, helix D prefusion and DE turn postfusion; pink, helix E; teal, loop F; purple, helix G; orange, C-terminal leash. Transmembrane domains (TMDs) are shown in green. HA1 is not seen in the postfusion structure. (b) Class II: dengue virus E in pre- (left, PDB 4UTB, side view) and postfusion (right, PDB 1OK8) conformations. In the left panel (prefusion), one E ectodomain monomer is shown in gray and the other is coded with domains I, II, and III in yellow, blue, and purple, respectively; the fusion loops (FLs) are shown in red, and the E TMDs are depicted in green. The companion protein, precursor membrane (prM), is not shown. All class II fusion proteins, including those involved in eukaryotic and archaeal fusion (187, 188), have the same basic architecture. (c) Class III: human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gB is shown in pre- (PDB 7KDP, left two panels) and postfusion (PDB 7KDD) conformations; an excised monomer is shown on the far left. Domains I, II, III, IV, and V of one monomer are shown in blue, magenta, teal, orange, and yellow, respectively. The membrane proximal external region (MPER) is in purple, the TMD in green, and the FLs in red. Cytoplasmic tails are not shown in any panels. See Supplemental Figure Legend 2 for more information and additional references.
