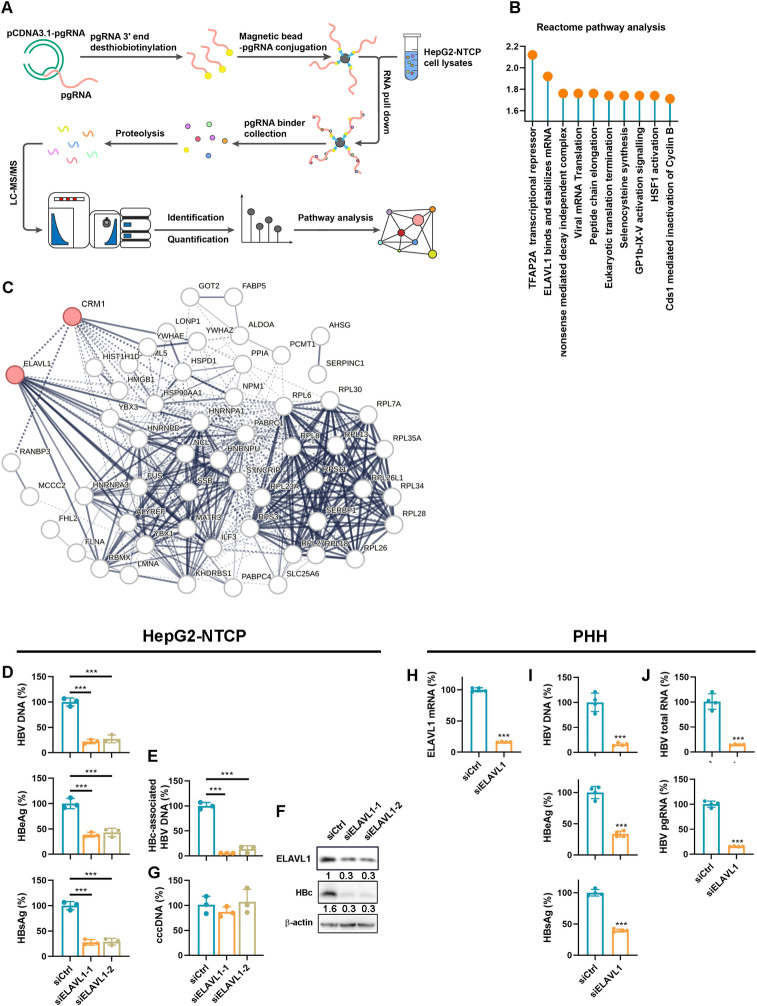
Fig 1. ELAVL1 supports HBV replication.
(A) Work flow of the RNA pulldown-LC-MS/MS. (B) Reactome pathway analysis for the pgRNA binders. (C) Network analysis for the pgRNA binding proteins. (D-G) HepG2-NTCP cells were transfected with ELAVL1 targeted siRNA. The cells were infected with HBV at an MOI = 200 and were maintained with DMEM medium supplemented with 2.5% DMSO for 5 days. (D) Levels of HBV DNA in supernatants were determined by qPCR (% of siCtrl). Secreted HBeAg and HBsAg levels were determined by ELISA (% of siCtrl). (E and G) Levels of intracellular HBc-associated DNA and HBV cccDNA were determined by qPCR (% of siCtrl). (F) Levels of ELAVL1 and HBc were determined by WB. (H-J) The primary human hepatocytes were transfected with ELAVL1 targeted siRNA 2 days before HBV infection (MOI = 200). Samples were collected 5days post HBV infection. (H) Knockdown efficiency was evaluated by qPCR (% of siCtrl). (I) The levels of HBV DNA in culture supernatant were determined by qPCR (% of siCtrl). The levels of HBeAg and HBsAg in culture supernatant were determined by ELISA (% of siCtrl). (J) The levels of intracellular HBV RNA were assessed by qPCR. Graphs were shown as mean ± SD. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001.