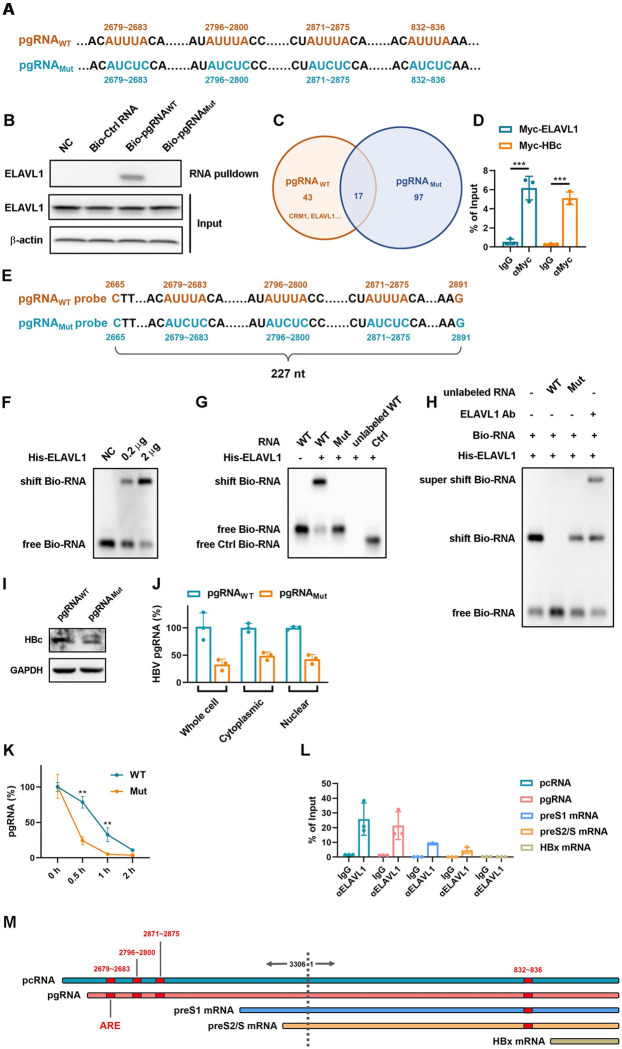
Fig 4. AU-rich elements in HBV RNAs are essential for ELAVL1 binding.
(A) Sequence of wild type pgRNA and mutant pgRNA used for RNA pulldown. (B) HepG2-NTCP cell lysates were incubated with biotinylated pgRNA or its mutant coated magnetic beads to pull down binding proteins. Levels of ELAVL1 in beads elutes were detected by WB. (C) Venn diagram of pgRNA and its mutant binders identified by RNA pulldown-LC-MS/MS. (D) Myc-ELAVL1 and Myc-HBc were co-transfected with pCDNA3.1-T7-pgRNA into Huh7 cells respectively. RIP assay was conducted to investigate interaction of ELAVL1-pgRNA and HBc-pgRNA. (E) Schematic diagram of pgRNA probe (227nt) and its mutant used for REMSA. (F) In vitro expressed and purified ELAVL1 were incubated with biotin labeled pgRNA probes. The samples were subjected to REMSA assay to detect the pgRNA probe and ELAVL1 binding. (G) The biotin labeled pgRNAAUUUA to AUCUC probe or wild type pgRNA probe was incubated with in vitro purified ELAVL1. REMSA assay was performed to detected pgRNA and ELAVL1 binding. Unlabeled wild type pgRNA probe and biotin labeled IRE1 probe as control. (H) Before biotin labeled pgRNA probe incubation, unlabeled pgRNA probe or the mutant was incubated with ELAVL1 (for cold compete). Before biotin labeled pgRNA probe incubation, the purified ELAVL1 was incubated with ELAVL1 targeted antibody (for super shift assay). The samples were subjected to REMSA assay for biotin labeled pgRNA probe and ELAVL1 binding detection. (I and J) Huh7 cells were transfected with pgRNA or its mutant (mutation site as indicated in A) expressing plasmid. (I) Levels of HBc expression were determined by WB. (J) Subcellular levels of HBV mRNA in cytoplasm and nucleus were determined by qPCR (% of WT). (K) The cells were treated with 10 nM Actinomycin D for times as indicated. Levels of pgRNA were determined by qPCR (normalized to Cp value of pCDNA3.1-pgRNAWT or pCDNA3.1-pgRNAMut, % of 0 hour). (L) The plasmids expressing pcRNA, pgRNA, PreS1 mRNA, PreS2/S mRNA, and HBx mRNA were transfected into Huh7 cells respectively. RIP assay was conducted to investigate their binding ability to ELAVL1. (M) Sequence analysis for AREs in HBV RNAs.