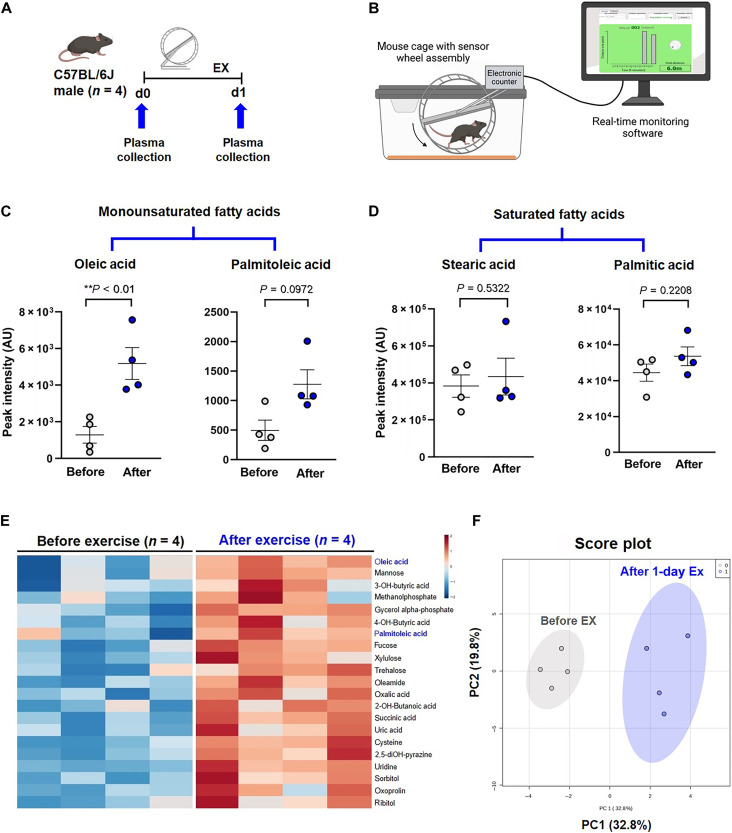
Fig. 3. Exercise alters catalysis of lipid metabolites.
(A) A schematic representation of the animal exercise (EX) protocol. Plasma was collected from the wild-type male C57BL/6J before and after 24 hours of voluntary wheel running for metabolomic analysis (n = 4 male mice for each group). d, day. (B) The voluntary wheel running system provided real-time monitoring of rodent running activity (figure generated with Biorender.com). (C) Twenty-four hours of exercise increased OA and PA; however, the latter did not reach statistical significance (OA: **P < 0.01 versus before exercise, paired t test, n = 4). (D) Exercise did not change the plasma levels of SFA stearic and palmitic acid. AU, arbitrary units. (E) Heatmap of plasma metabolites before and after exercise reveals that OA was elevated in all four mice after normalization and scaling using the Pareto method. (F) Score plots by the PCA support the 90% confidence intervals before and after exercise. PC, principal component.