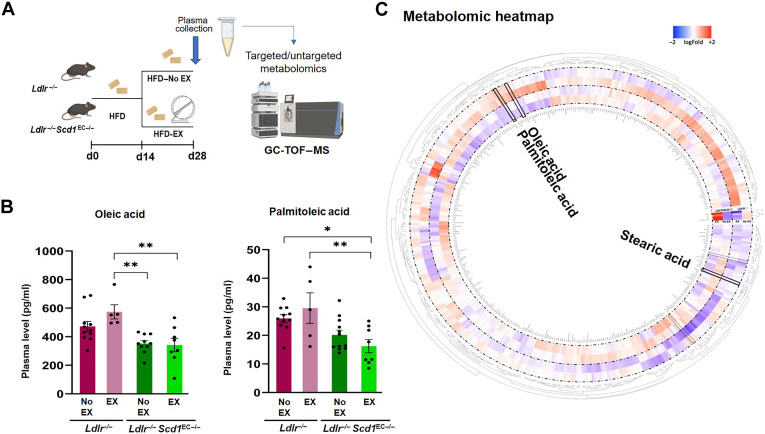
Fig. 6. Exercise-mediated lipid metabolites OA and PA are reduced in mice with endothelial-specific Scd1 deletion.
(A) The experimental protocol depicts the Ldlr−/− mice that were crossed with Cdh5Cre; Scd1flox/flox to generate endothelial-specific SCD1 deletion (Ldlr−/− Scd1EC−/−). Adult mice at 8 weeks were fed HFD for 14 days. The HFD-fed mice were then divided into exercise (EX) and no exercise (No EX) arms for additional 14 days while continuing HFD. GC-TOF-MS, gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry. (B) The absolute plasma OA concentration was elevated after exercise in the Ldlr−/− mice, whereas OA concentration was reduced and remained reduced after exercise in the Ldlr−/− Scd1EC−/− mice. The plasma concentration of PA also followed a similar trend, suggesting that exercise activates SCD1 to catalyze OA and PA (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01; n = 4 to 12; two-way ANOVA; each dot represents an individual animal). (C) Circular heatmap of untargeted metabolomic analysis captures the known and unknown identity (ID) metabolites and highlights changes in OA and PA after normalization and scaling using the Pareto method. The circular heatmap further supports that Scd1 deletion resulted in a decrease in both OA and PA. Circular heatmap was generated with Circos R package.