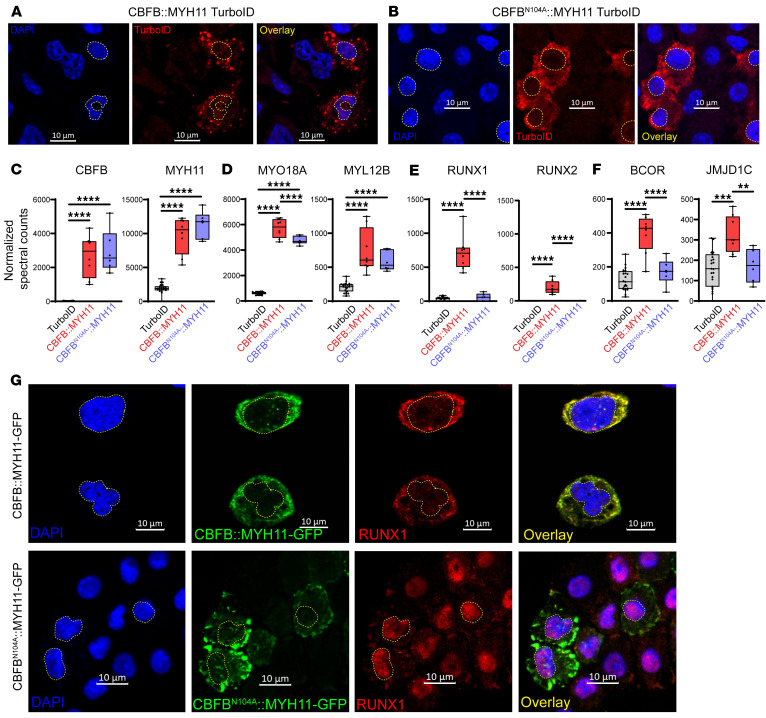
Figure 6. The CBFB N104 residue mediates CBFB interaction with RUNX proteins.
(A) Immunofluorescence of CBFB::MYH11-TurboID–transduced HSPCs (A) or CBFBN104A::MYH11-TurboID–transduced HSPCs (B) demonstrates cytoplasmic localization of each. DAPI staining (blue) identifies nuclei, which are outlined with yellow dotted lines. TurboID is detected in red. Images are representative of 2 experiments. Scale bars: 10 μm. (C) Normalized spectral counts of CBFB and MYH11 in protein lysates from CBFB::MYH11-TurboID (n = 8) and CBFBN104A::MYH11-TurboID (n = 6) are not significantly different. One-way ANOVA between all samples, ****P < 0.0001, nonsignificant comparisons not labeled. Each point represents an individual sample, bar indicates mean, box indicates 95% confidence interval, and whiskers indicate value range. (D) Interactions between myosin-related proteins are maintained in CBFBN104A::MYH11-TurboID samples. One-way ANOVA between all samples, ****P < 0.0001, nonsignificant comparisons not labeled. (E) CBFBN104A::MYH11 disrupts the interaction with RUNX1. One-way ANOVA between all samples, ****P < 0.0001, nonsignificant comparisons not labeled. (F) CBFBN104A::MYH11 disrupts interactions between CBFB::MYH11 and other nuclear proteins, suggesting that these interactions are also mediated by RUNX-CBFB binding. One-way ANOVA between all samples, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, nonsignificant comparisons not labeled. (G) Primary murine hematopoietic cells were transduced with retroviruses encoding CBFB::MYH11-GFP (top) or CBFBN104A::MYH11-GFP (bottom). Note that while CBFB::MYH11-GFP and CBFBN104A::MYH11-GFP are both cytoplasmic, RUNX1 relocalizes to the nucleus in cells expressing CBFBN104A::MYH11-GFP. Images are representative of 2–4 experiments. Scale bars: 10 μm.