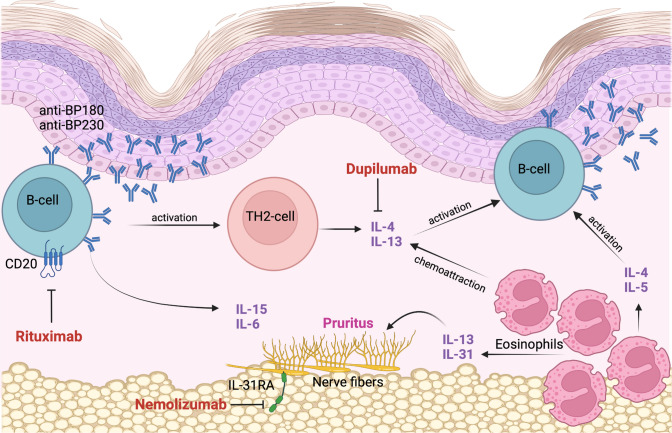
Fig. 2.
Th2 pathways are considered the primary triggers for antibody production in BP. Rituximab targets the CD20 transmembrane receptor expressed on the surface of B-lymphocytes. It induces a B-lymphocyte depletion and prevents the differentiation of B-lymphocytes into antibody-secreting plasma cells. Th2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-13 play an important role in eosinophil chemoattraction. Autoreactive Th2 cells stimulate B-cell autoantibody production and participate in the recruitment and activation of eosinophils. Eosinophils also contribute to the maintenance of Th2-type inflammatory responses by further producing IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. IL-13 can directly stimulate peripheral nerve fibers and indirectly recruit IL-31-secreting eosinophils to the site of skin lesions, and is therefore involved in BP-associated itch. Dupilumab can inhibit IL-4 and IL-13 signaling. It downregulates eosinophil chemotaxins and inhibits Th2-associated chemokine activity, B-cell proliferation and autoantibody production. Dupilumab may further improve pruritus in BP by directly reducing IL-13 and by indirectly downregulating IL-31 production by eosinophils. Nemolizumab is an anti-IL-31 receptor A antibody that can contribute to a great reduction of pruritus. BP bullous pemphigoid, IL interleukin, CD20 cluster of differentiation 20, Th2 type 2 helper