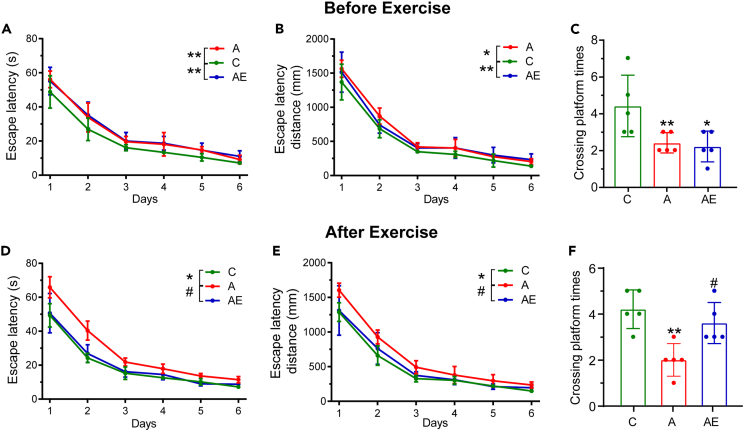
Figure 1.
Exercise alleviated the spatial learning and memory ability of rats damaged by D-gal, which were detected by MWM test
(A), (B), and (C) were tested before exercise intervention.
(D), (E), and (F) were tested after exercise intervention (n = 5, Data were represented as mean ± standard deviation and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA analysis of GraphPad Prism 9. ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05 indicate significant difference compared with C group, respectively; #p < 0.05 indicates a significant difference compared with A group. The comparison of (A), (B), (D), and (E) was done with the average of data for the entire period during the navigation phase.(A) and (D) Escape latency of rats on 1st–6th days in the navigation phase (B) and (E) Escape latency distance of rats on 1st–6th days in the navigation phase (C) and (F) The times of crossing platform of rats on the 7th day in the spatial exploration phase. See also Figure S1.