Extended Data Fig. 2 |. Interaction and localization of pulse-labeled ribosomal proteins with Sis1.
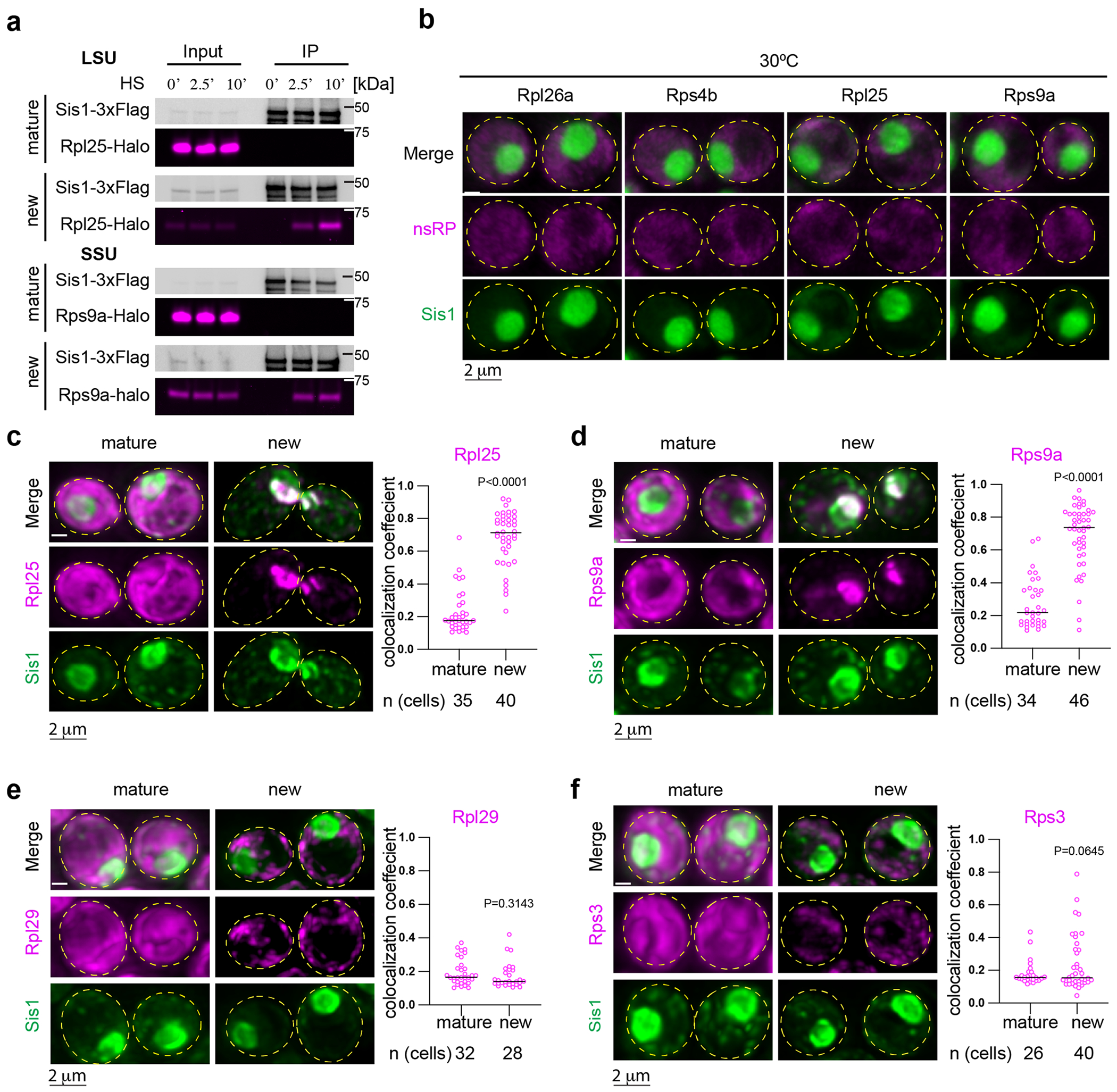
(a) IP of Sis1-3xFlag and either mature or new Rpl25-Halo and Rps9a-Halo from cells left unstressed or heat shocked at 39 °C for the indicated times. n = 2 biologically independent experiment. (b) In the absence of heat shock, pulse-labeled RPs localize immediately to the cytosol. Micrograph represents data obtained from 3 biologically independent experiments. (c) Left Panel: Lattice light sheet live imaging of yeast under heat shock (39 °C, 10 min) expressing Sisl-mVenus and labeled for either new or mature Rpl25-Halo. Right Panel: Dot plot representing the colocalization coefficient (Mander’s overlap coefficient) of Sis1-mVenus with either mature or new Rpl25-Halo in heat shocked cells (39 °C, 10 min). n = number of cells pooled from 3 biologically independent replicates. (d) As in (c) but for Rps9a-Halo. n = number of cells pooled from 3 biologically independent replicates. (e) As in (c) but for the latejoining subunit Rpl29-Halo. n = number of cells pooled from 3 biologically independent replicates. (f) As in (c) but for the late joining subunit Rps3-Halo. n = number of cells pooled from 3 biologically independent replicates. P values were calculated with unpaired two-tailed Welch’s t-test.
